Electroacupuncture and rosiglitazone combined therapy as a means of treating insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23983807
- PMCID: PMC3745852
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/969824
Electroacupuncture and rosiglitazone combined therapy as a means of treating insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
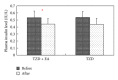
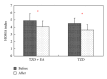
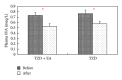
Aims. To evaluate the efficacy of rosiglitazone (TZD) and electroacupuncture (EA) combined therapy as a treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients by randomized single-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Methods. A total of 31 newly diagnostic T2DM patients, who fulfilled the study's eligibility criteria, were recruited. The individuals were randomly assigned into two groups, the control group (TZD, N = 15) and the experimental group (TZD + EA, N = 16). Changes in their plasma free fatty acid (FFA), glucose, and insulin levels, together with their homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) indices, were statistically compared before and after treatment. Hypoglycemic activity (%) was also compared between these two groups. Results. There was no significant difference in hypoglycemic activity between the TZD and TZD + EA group. The effectiveness of the combined therapy seems to derive from an improvement in insulin resistance and a significant lowering of the secreted insulin rather than the effect of TZD alone on T2DM. The combined treatment had no significant adverse effects. A lower plasma FFA concentration is likely to be the mechanism that causes this effect. Conclusion. This combined therapy seems to suppress endogenous insulin secretion by improving insulin resistance via a mechanism involving a reduction in plasma FFA. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01577095.
Figures
References
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine. 1998;15:539–553. - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414(6865):782–787. - PubMed
-
- Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006;368(9548):1681–1688. - PubMed
-
- Goodyear LJ, Kahn BB. Exercise, glucose transport, and insulin sensitivity. Annual Review of Medicine. 1998;49:235–261. - PubMed
-
- Hunter SJ, Garvey WT. Insulin action and insulin resistance: diseases involving defects in insulin receptors, signal transduction, and the glucose transport effector system. American Journal of Medicine. 1998;105(4):331–345. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

