Safety of thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: a review of complications, risk factors, and newer technologies
- PMID: 23983849
- PMCID: PMC3726129
- DOI: 10.1177/1941875211408731
Safety of thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: a review of complications, risk factors, and newer technologies
Abstract
Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (r-tPA) was approved for use in acute ischemic stroke in the United States in 1996. Approximately 2% to 5% of patients with acute ischemic stroke receive r-tPA. Complications related to intravenous r-tPA include symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, major systemic hemorrhage, and angioedema in approximately 6%, 2%, and 5% of patients, respectively. Risk factors for symptomatic hemorrhage include age, male gender, obesity, increased stroke severity, diabetes, hyperglycemia, uncontrolled hypertension, combination antiplatelet use, large areas of early ischemic change, atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure, and leukoariosis. A risk factor for angioedema is the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Risk assessment scores, novel imaging strategies, and telemedicine may offer methods of optimizing the risk-benefit ratio.
Keywords: safety; stroke; thrombolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared a potential conflict of interest (e.g. a financial relationship with the commercial organizations or products discussed in this article) as follows: Drs Miller and Simpson have nothing to report. Dr Silver has received consulting fees from Abbott Vascular and has served as an expert for stroke medical malpractice defense.
Figures

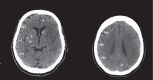
References
-
- Barber PA, Zhang J, Demchuk AM, Hill MD, Buchan AM. Why are stroke patients excluded from TPA therapy? An analysis of patient eligibility. Neurology. 2001;56(8):1015–1020 - PubMed
-
- Deng YZ, Reeves MJ, Jacobs BS, et al. IV tissue plasminogen activator use in acute stroke: experience from a statewide registry. Neurology. 2006;66(3):306–312 - PubMed
-
- Kase CS, Furlan AJ, Wechsler LR, et al. Cerebral hemorrhage after intra-arterial thrombolysis for ischemic stroke: the PROACT II trial. Neurology. 2001;57(9):1603–1610 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
