Tobacco Smoking and Lung Cancer: Perception-changing facts
- PMID: 23984018
- PMCID: PMC3749017
- DOI: 10.12816/0003255
Tobacco Smoking and Lung Cancer: Perception-changing facts
Abstract
Tobacco smoking remains the most established cause of lung carcinogenesis and other disease processes. Over the last 50 years, tobacco refinement and the introduction of filters have brought a change in histology, and now adenocarcinoma has become the most prevalent subtype. Over the last decade, smoking also has emerged as a strong prognostic and predictive patient characteristic along with other variables. This article briefly reviews scientific facts about tobacco, and the process and molecular pathways involved in lung carcinogenesis in smokers and never-smokers. The evidence from randomised trials about tobacco smoking's impact on lung cancer outcomes is also reviewed.
Keywords: Carcinogens; EML4 ALK fusion protein, human; K-Ras Gene; Lung Neoplasms; Nicotine; Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor; Tobacco Smoking.
Figures

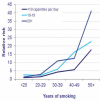

References
-
- Wikipedia. Smoking. From: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smoking#cite_ref-14 Accessed: Nov 2012.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2008. From: World Health Organization. From http://www.who.int/tobacco/mpower/mpower_report_full_2008.pdf Accessed: Nov 2012.
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2012. From http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveillance/docum... Accessed: Oct 2012.
-
- United States Department of Health & Human Services. The Health Consequences of Using Smokeless Tobacco: A report of the Advisory Committee to the Surgeon General. From: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveilance/docume... Accessed: Nov 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
