Cathepsin B contributes to autophagy-related 7 (Atg7)-induced nod-like receptor 3 (NLRP3)-dependent proinflammatory response and aggravates lipotoxicity in rat insulinoma cell line
- PMID: 23986436
- PMCID: PMC3798478
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.494286
Cathepsin B contributes to autophagy-related 7 (Atg7)-induced nod-like receptor 3 (NLRP3)-dependent proinflammatory response and aggravates lipotoxicity in rat insulinoma cell line
Abstract
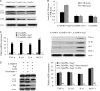
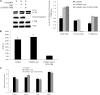
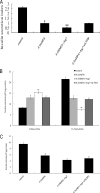
Impairment of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion caused by the lipotoxicity of palmitate was found in β-cells. Recent studies have indicated that defects in autophagy contribute to pathogenesis in type 2 diabetes. Here, we report that autophagy-related 7 (Atg7) induced excessive autophagic activation in INS-1(823/13) cells exposed to saturated fatty acids. Atg7-induced cathepsin B (CTSB) overexpression resulted in an unexpected significant increase in proinflammatory chemokine and cytokine production levels of IL-1β, monocyte chemotactic protein-1, IL-6, and TNF-α. Inhibition of receptor-interacting protein did not affect the inflammatory response, ruling out involvement of necrosis. CTSB siRNA suppressed the inflammatory response but did not affect apoptosis significantly, suggesting that CTSB was a molecular linker between autophagy and the proinflammatory response. Blocking caspase-3 suppressed apoptosis but did not affect the inflammatory response, suggesting that CTSB induced inflammatory effects independently of apoptosis. Silencing of Nod-like receptor 3 (NLRP3) completely abolished both IL-1β secretion and the down-regulation effects of Atg7-induced CTSB overexpression on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion impairment, thus identifying the NLRP3 inflammasome as an autophagy-responsive element in the pancreatic INS-1(823/13) cell line. Combined together, our results indicate that CTSB contributed to the Atg7-induced NLRP3-dependent proinflammatory response, resulting in aggravation of lipotoxicity, independently of apoptosis in the pancreatic INS-1(823/13) cell line.
Keywords: Autophagy; Cytokine; Glucose Metabolism; Inflammation; Insulin Resistance; Pancreatic Islets.
Figures




References
-
- Shao S., Liu Z., Yang Y., Zhang M., Yu X. (2010) SREBP-1c, Pdx-1, and GLP-1R involved in palmitate-EPA regulated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in INS-1 cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 111, 634–642 - PubMed
-
- Gregor M. F., Hotamisligil G. S. (2011) Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 29, 415–445 - PubMed
-
- Donath M. Y., Shoelson S. E. (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 98–107 - PubMed
-
- Festa A., D'Agostino R., Jr., Tracy R. P., Haffner S. M. (2002) Elevated levels of acute-phase proteins and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 predict the development of type 2 diabetes: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes 51, 1131–1137 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

