Hydrocele of the canal of Nuck: imaging findings
- PMID: 23986837
- PMCID: PMC3738346
- DOI: 10.1258/arsr.2012.110016
Hydrocele of the canal of Nuck: imaging findings
Abstract
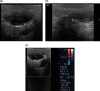
The hydrocele of the canal of Nuck is quite a rare condition and results from the failure of obliteration of the distal portion of evaginated parietal peritoneum within the inguinal canal which forms a sac containing fluid. It generally presents with painless inguinal swelling. Ultrasonography and MRI is plays an important role to differentiate from the other conditions presenting with inguinal swelling. We present the imaging findings of a case in 5-year-old girl.
Keywords: Hydrocele; MRI; canal of Nuck; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Shadbolt CL, Heinze SB, Dietrich RB Imaging of groin masses: inguinal anatomy and pathologic conditions revisited. Radiographics 2001;21:S261–71 - PubMed
-
- Anderson CC, Broadie TA, Mackey JE, et al. Hydrocele of the canal of Nuck: ultrasound appearance. Am Surg 1995;61:959–61 - PubMed
-
- Tubbs RS, Loukas M, Shoja MM, et al. Indirect inguinal hernia of the urinary bladder through a persistent canal of Nuck: case report. Hernia 2007;11:287–8 - PubMed
-
- Patil SN, Bielamowicz K Female hydrocele of canal of nuck. J Ark Med Soc 2010;107:38–9 - PubMed
-
- Block RE Hydrocele of the canal of nuck. A report of five cases. Obstet Gynecol 1975;45:464–6 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
