Poly(iohexol) nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging
- PMID: 23987119
- PMCID: PMC4232444
- DOI: 10.1021/ja405196f
Poly(iohexol) nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging
Abstract
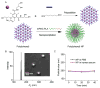
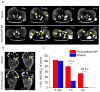
Biocompatible poly(iohexol) nanoparticles, prepared through cross-linking of iohexol and hexamethylene diisocyanate followed by coprecipitation of the resulting cross-linked polymer with mPEG-polylactide, were utilized as contrast agents for in vivo X-ray computed tomography (CT) imaging. Compared to conventional small-molecule contrast agents, poly(iohexol) nanoparticles exhibited substantially protracted retention within the tumor bed and a 36-fold increase in CT contrast 4 h post injection, which makes it possible to acquire CT images with improved diagnosis accuracy over a broad time frame without multiple administrations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contrast-enhanced microcomputed tomography using intraperitoneal contrast injection for the assessment of tumor-burden in liver metastasis models.Invest Radiol. 2008 Jul;43(7):488-95. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318172f5b5. Invest Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18580331
-
Hyaluronic acid-coated ultrasmall BiOI nanoparticles as a potentially targeted contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Sep 30;217:668-676. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.094. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35850269
-
Noninvasive monitoring of local drug release using X-ray computed tomography: optimization and in vitro/in vivo validation.J Pharm Sci. 2003 Feb;92(2):289-96. doi: 10.1002/jps.10295. J Pharm Sci. 2003. PMID: 12532379
-
[New non-ionic monomeric and dimeric contrasting agents in radiology].Vestn Rentgenol Radiol. 1998 Sep-Oct;(5):56-7. Vestn Rentgenol Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9987947 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
-
Nano-sized CT contrast agents.Adv Mater. 2013 May 21;25(19):2641-60. doi: 10.1002/adma.201300081. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Adv Mater. 2013. PMID: 23553799 Review.
Cited by
-
Opportunities for new CT contrast agents to maximize the diagnostic potential of emerging spectral CT technologies.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017 Apr;113:201-222. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017. PMID: 27620496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic RGD-Functionalized and Disulfide-Crosslinked Iodine-Rich Polymersomes as a Robust and Smart Theranostic Agent for Targeted CT Imaging and Chemotherapy of Tumor.Theranostics. 2019 Oct 17;9(26):8061-8072. doi: 10.7150/thno.37184. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31754381 Free PMC article.
-
Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as photoacoustic molecular imaging probes.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017 Mar;9(2):10.1002/wnan.1418. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1418. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27346564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterial-based contrast agents.Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2023;3:30. doi: 10.1038/s43586-023-00211-4. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2023. PMID: 38130699 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted tumor dual mode CT/MR imaging using multifunctional polyethylenimine-entrapped gold nanoparticles loaded with gadolinium.Drug Deliv. 2018 Nov;25(1):178-186. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1422299. Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29301434 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

