Robustly passivated, gold nanoaperture arrays for single-molecule fluorescence microscopy
- PMID: 23987563
- PMCID: PMC4748375
- DOI: 10.1021/nn403447s
Robustly passivated, gold nanoaperture arrays for single-molecule fluorescence microscopy
Abstract
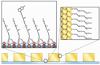
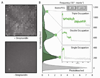
The optical confinement generated by metal-based nanoapertures fabricated on a silica substrate has recently enabled single-molecule fluorescence measurements to be performed at physiologically relevant background concentrations of fluorophore-labeled biomolecules. Nonspecific adsorption of fluorophore-labeled biomolecules to the metallic cladding and silica bottoms of nanoapertures, however, remains a critical limitation. To overcome this limitation, we have developed a selective functionalization chemistry whereby the metallic cladding of gold nanoaperture arrays is passivated with methoxy-terminated, thiol-derivatized polyethylene glycol (PEG), and the silica bottoms of those arrays are functionalized with a binary mixture of methoxy- and biotin-terminated, silane-derivatized PEG. This functionalization scheme enables biotinylated target biomolecules to be selectively tethered to the silica nanoaperture bottoms via biotin-streptavidin interactions and reduces the nonspecific adsorption of fluorophore-labeled ligand biomolecules. This, in turn, enables the observation of ligand biomolecules binding to their target biomolecules even under greater than 1 μM background concentrations of ligand biomolecules, thereby rendering previously impracticable biological systems accessible to single-molecule fluorescence investigations.
Figures
References
-
- Fersht AR. Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science. New York: W.H. Freeman and Co.; 1999. pp. 293–368.
-
- Levene MJ, Korlach J, Turner SW, Foquet M, Craighead HG, Webb WW. Zero-Mode Waveguides for Single-molecule Analysis at High Concentrations. Science. 2003;299:682–686. - PubMed
-
- Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF. Imaging Intracellular Fluorescent Proteins at Nanometer Resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

