Early results of the Swiss Multicentre Bypass or Sleeve Study (SM-BOSS): a prospective randomized trial comparing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
- PMID: 23989054
- PMCID: PMC3888472
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a67426
Early results of the Swiss Multicentre Bypass or Sleeve Study (SM-BOSS): a prospective randomized trial comparing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
Abstract
Objective: Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) has been proposed as an effective alternative to the current standard procedure, laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB). Prospective data comparing both procedures are rare. Therefore, we performed a randomized clinical trial assessing the effectiveness and safety of these 2 operative techniques.
Methods: Two hundred seventeen patients were randomized at 4 bariatric centers in Switzerland. One hundred seven patients underwent LSG using a 35-F bougie with suturing of the stapler line, and 110 patients underwent LRYGB with a 150-cm antecolic alimentary and a 50-cm biliopancreatic limb. The mean body mass index of all patients was 44 ± 11.1 kg/m, the mean age was 43 ± 5.3 years, and 72% were female.
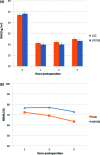
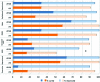
Results: The 2 groups were similar in terms of body mass index, age, sex, comorbidities, and eating behavior. The mean operative time was less for LSG than for LRYGB (87 ± 52.3 minutes vs 108 ± 42.3 minutes; P = 0.003). The conversion rate was 0.9% in both groups. Complications (<30 days) occurred more often in LRYGB than in LSG (17.2% vs 8.4%; P = 0.067). However, the difference in severe complications did not reach statistical significance (4.5% for LRYGB vs 1% for LSG; P = 0.21). Excessive body mass index loss 1 year after the operation was similar between the 2 groups (72.3% ± 22% for LSG and 76.6% ± 21% for LRYGB; P = 0.2). Except for gastroesophageal reflux disease, which showed a higher resolution rate after LRYGB, the comorbidities and quality of life were significantly improved after both procedures.
Conclusions: LSG was associated with shorter operation time and a trend toward fewer complications than with LRYGB. Both procedures were almost equally efficient regarding weight loss, improvement of comorbidities, and quality of life 1 year after surgery. Long-term follow-up data are needed to confirm these facts.
Figures
References
-
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–1737 - PubMed
-
- Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2683–2693 - PubMed
-
- Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1577–1585 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

