Crystallization studies of the keratin-like domain from Arabidopsis thaliana SEPALLATA 3
- PMID: 23989147
- PMCID: PMC3758147
- DOI: 10.1107/S174430911302006X
Crystallization studies of the keratin-like domain from Arabidopsis thaliana SEPALLATA 3
Abstract
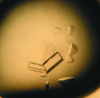
In higher plants, the MADS-box genes encode a large family of transcription factors (TFs) involved in key developmental processes, most notably plant reproduction, flowering and floral organ development. SEPALLATA 3 (SEP3) is a member of the MADS TF family and plays a role in the development of the floral organs through the formation of multiprotein complexes with other MADS-family TFs. SEP3 is divided into four domains: the M (MADS) domain, involved in DNA binding and dimerization, the I (intervening) domain, a short domain involved in dimerization, the K (keratin-like) domain important for multimeric MADS complex formation and the C (C-terminal) domain, a largely unstructured region putatively important for higher-order complex formation. The entire K domain along with a portion of the I and C domains of SEP3 was crystallized using high-throughput robotic screening followed by optimization. The crystals belonged to space group P2(1)2(1)2, with unit-cell parameters a = 123.44, b = 143.07, c = 49.83 Å, and a complete data set was collected to 2.53 Å resolution.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; MADS-box; SEPALLATA 3; keratin-like domain; transcription factors.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla, E. R., Liljegren, S. J., Pelaz, S., Gold, S. E., Burgeff, C., Ditta, G. S., Vergara-Silva, F. & Yanofsky, M. F. (2000). Plant J. 24, 457–466. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A. & Theissen, G. (2003). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 29, 464–489. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., Winter, K.-U., Meyer, B., Saedler, H. & Theissen, G. (2000). Mol. Biol. Evol. 17, 1425–1434. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

