Prevention of carcinogenesis and development of gastric and colon cancers by 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one (Phx-3): direct and indirect anti-cancer activity of Phx-3
- PMID: 23989604
- PMCID: PMC3794742
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140917573
Prevention of carcinogenesis and development of gastric and colon cancers by 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one (Phx-3): direct and indirect anti-cancer activity of Phx-3
Abstract
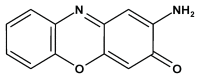
2-Aminophenoxazine-3-one (Phx-3), an oxidative phenoxazine, exerts strong anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines originating from different organs, in vitro. This article reviews new aspects for the prevention of carcinogenesis and development of gastric and colon cancers by Phx-3, based on the strong anticancer effects of Phx-3 on gastric and colon cancer cell lines (direct anticancer effects of Phx-3 for preventing development of cancer), the bacteriocidal effects of Phx-3 against Helicobacter pylori associated with carcinogenesis of gastric cancer (indirect anticancer effects for preventing carcinogenesis of gastric cancer), and the proapoptotic activity of Phx-3 against human neutrophils involved in the incidence of ulcerative colitis associated with a high colon cancer risk (indirect anticancer effects for preventing carcinogenesis of colon cancer).
Figures
References
-
- Anzai K., Isono K., Okuma K., Suzuki S. The new antibiotics, questiomycins A and B. J. Antibiotics. 1960;13:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Tomoda A., Yamaguchi J., Kojima H., Amemiya H., Yoneyama Y. Mechanism of o-aminophenol metabolism in human erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1986;196:44–48. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu S., Suzuki M., Miyazawa K., Yokoyama T., Ohyashiki K., Miyazaki K., Abe A., Tomoda A. Differentiation and apoptosis in human malignant melanoma G-361 cells induced by 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one. Oncol. Rep. 2005;14:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Kato S., Shirato K., Imaizumi K., Toyota H., Mizuguchi J., Odawara M., Che X-F., Akiyama S., Abe A., Tomoda A. Anticancer effects of phenoxazine derivatives combined with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand on pancreatic cancer cell lines, KLM-1 and MIA-PaCa-2. Oncol. Rep. 2006;15:843–848. - PubMed
-
- Shirato K., Imaizumi K., Miyazawa K., Takasaki A., Mizuguchi J., Che XF., Akiyama S., Tomoda A. Apoptosis induction preceded by mitochondrial depolarization in multiple myeloma cell line U266 by 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008;31:62–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical