Steap4 plays a critical role in osteoclastogenesis in vitro by regulating cellular iron/reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) activation
- PMID: 23990467
- PMCID: PMC3798475
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.478750
Steap4 plays a critical role in osteoclastogenesis in vitro by regulating cellular iron/reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) activation
Abstract
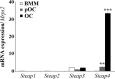
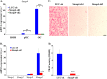
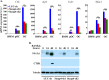
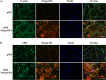
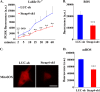
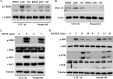
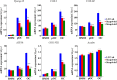
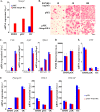
Iron is essential for osteoclast differentiation, and iron overload in a variety of hematologic diseases is associated with excessive bone resorption. Iron uptake by osteoclast precursors via the transferrin cycle increases mitochondrial biogenesis, reactive oxygen species production, and activation of cAMP response element-binding protein, a critical transcription factor downstream of receptor activator of NF-κB-ligand-induced calcium signaling. These changes are required for the differentiation of osteoclast precursors to mature bone-resorbing osteoclasts. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating cellular iron metabolism in osteoclasts remain largely unknown. In this report, we provide evidence that Steap4, a member of the six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate (Steap) family proteins, is an endosomal ferrireductase with a critical role in cellular iron utilization in osteoclasts. Specifically, we show that Steap4 is the only Steap family protein that is up-regulated during osteoclast differentiation. Knocking down Steap4 expression in vitro by lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNAs inhibits osteoclast formation and decreases cellular ferrous iron, reactive oxygen species, and the activation of cAMP response element-binding protein. These results demonstrate that Steap4 is a critical enzyme for cellular iron uptake and utilization in osteoclasts and, thus, indispensable for osteoclast development and function.
Keywords: Bone; Iron Metabolism; Mitochondria; Osteoclast; Oxidative Stress.
Figures

References
-
- Boyle W. J., Simonet W. S., Lacey D. L. (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423, 337–342 - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum S. L. (2000) Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science 289, 1504–1508 - PubMed
-
- Helfrich M. H. (2003) Osteoclast diseases. Microscopy Res. Tech. 61, 514–532 - PubMed
-
- Suda T., Takahashi N., Udagawa N., Jimi E., Gillespie M. T., Martin T. J. (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr. Rev. 20, 345–357 - PubMed
-
- Ross F. P., Teitelbaum S. L. (2005) αvβ3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Partners in osteoclast biology. Immunol. Rev. 208, 88–105 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

