Impact of flavonoids on matrix metalloproteinase secretion and invadopodia formation in highly invasive A431-III cancer cells
- PMID: 23991004
- PMCID: PMC3749203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071903
Impact of flavonoids on matrix metalloproteinase secretion and invadopodia formation in highly invasive A431-III cancer cells
Abstract
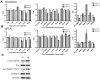
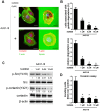
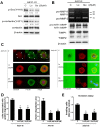
Metastasis is a major cause of mortality in cancer patients. Invadopodia are considered to be crucial structures that allow cancer cells to penetrate across the extracellular matrix (ECM) by using matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Previously, we isolated a highly invasive A431-III subline from parental A431 cells by Boyden chamber assay. The A431-III cells possess higher invasive and migratory abilities, elevated levels of MMP-9 and an enhanced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype. In this study, we discovered that A431-III cells had an increased potential to form invadopodia and an improved capacity to degrade ECM compared with the original A431 cells. We also observed enhanced phosphorylation levels of cortactin and Src in A431-III cells; these phosphorylated proteins have been reported to be the main regulators of invadopodia formation. Flavonoids, almost ubiquitously distributed in food plants and plant food products, have been documented to exhibit anti-tumor properties. Therefore, it was of much interest to explore the effects of flavonoid antioxidants on the metastatic activity of A431-III cells. Exposure of A431-III cells to two potent dietary flavonoids, namely luteolin (Lu) and quercetin (Qu), caused inhibition of invadopodia formation and decrement in ECM degradation. We conclude that Lu and Qu attenuate the phosphorylation of cortactin and Src in A431-III cells. As a consequence, there ensues a disruption of invadopodia generation and the suppression of MMP secretion. These changes, in concert, bring about a reduction in metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA (2011) A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 331: 1559–1564. - PubMed
-
- Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1990) Metalloproteinases and cancer invasion. Semin Cancer Biol 1: 99–106. - PubMed
-
- Weaver AM (2006) Invadopodia: specialized cell structures for cancer invasion. Clin Exp Metastasis 23: 97–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

