Oleanolic acid suppresses migration and invasion of malignant glioma cells by inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 23991044
- PMCID: PMC3749117
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072079
Oleanolic acid suppresses migration and invasion of malignant glioma cells by inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
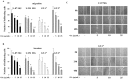
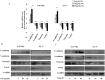
Mitogen-activated protein kinases/Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) pathway is essential for migration and invasion of malignant glioma. It is efficient to inhibit migration and invasion of glioma cells by targeting this pathway. Oleanolic acid (OA) has been well demonstrated to suppress survival, growth and angiogenesis of glioma cells. However, it is still unknown if OA affects the migration and invasion of glioma cells. We utilized U-87 MG glioma cell lines and primary glioma cells from patients to study the effect of OA on migration and invasion of glioma cells with multidisciplinary approaches. In this study, we found that OA significantly decreased the ability of glioma cells to migrate and invade. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of glioma cells was also suppressed by OA treatment. Furthermore, MAPK/ERK pathway was greatly inhibited in glioma cells under OA treatment. MAPK/ERK reactivation induced by a recombinant lentiviral vector, Lv-MEK, was able to rescue the inhibitory effect of OA on migration and invasion of glioma cells. Taken together, we provided evidences that OA was a MAPK/ERK pathway-targeting anti-tumor agent. Although the concentrations we used exceeded its physiological level, OA may be used to prevent migration and invasion of glioma cells by developing its derivatives with enhanced bioactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Omuro AM (2008) Exploring multi-targeting strategies for the treatment of gliomas. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 9: 1287–1295. - PubMed
-
- Zohrabian VM, Forzani B, Chau Z, Murali R, Jhanwar-Uniyal M (2009) Rho/ROCK and MAPK signaling pathways are involved in glioblastoma cell migration and proliferation. Anticancer Res 29: 119–123. - PubMed
-
- Nickl-Jockschat T, Arslan F, Doerfelt A, Bogdahn U, Bosserhoff A, et al. (2007) An imbalance between Smad and MAPK pathways is responsible for TGF-beta tumor promoting effects in high-grade gliomas. Int J Oncol 30: 499–507. - PubMed
-
- Song H, Moon A (2006) Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) promotes low-grade Hs683 glioma cell migration through JNK, ERK-1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Neurosci Res 56: 29–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

