In-cell NMR characterization of the secondary structure populations of a disordered conformation of α-synuclein within E. coli cells
- PMID: 23991082
- PMCID: PMC3753296
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072286
In-cell NMR characterization of the secondary structure populations of a disordered conformation of α-synuclein within E. coli cells
Abstract
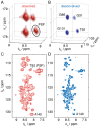
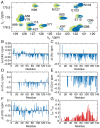
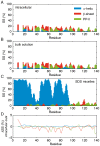
α-Synuclein is a small protein strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. We report here the use of in-cell NMR spectroscopy to observe directly the structure and dynamics of this protein within E. coli cells. To improve the accuracy in the measurement of backbone chemical shifts within crowded in-cell NMR spectra, we have developed a deconvolution method to reduce inhomogeneous line broadening within cellular samples. The resulting chemical shift values were then used to evaluate the distribution of secondary structure populations which, in the absence of stable tertiary contacts, are a most effective way to describe the conformational fluctuations of disordered proteins. The results indicate that, at least within the bacterial cytosol, α-synuclein populates a highly dynamic state that, despite the highly crowded environment, has the same characteristics as the disordered monomeric form observed in aqueous solution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cookson MR (2005) The biochemistry of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Biochem 74: 29–52 doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133400 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM (2006) Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu Rev Biochem 75: 333–366 doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.101304.123901 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Uversky VN, Li J, Souillac P, Millett IS, Doniach S, et al. (2002) Biophysical properties of the synucleins and their propensities to fibrillate: inhibition of alpha-synuclein assembly by beta- and gamma-synucleins. J Biol Chem 277: 11970–11978 doi:10.1074/jbc.M109541200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weinreb PH, Zhen W, Poon AW, Conway KA, Lansbury PT (1996) NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 35: 13709–13715 doi:10.1021/bi961799n - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eliezer D, Kutluay E, Bussell R, Browne G (2001) Conformational properties of alpha-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J Mol Biol 307: 1061–1073 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4538 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

