Development of hybrid small molecules that induce degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha and necrotic cell death in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23992566
- PMCID: PMC7654239
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12272
Development of hybrid small molecules that induce degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha and necrotic cell death in breast cancer cells
Abstract
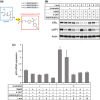
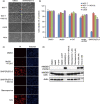
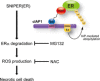
Manipulation of protein stability with small molecules has a great potential for both basic research and clinical therapy. Recently, we have developed a series of hybrid small molecules named SNIPER (Specific and Non-genetic IAP-dependent Protein ERaser) that induces degradation of target proteins via ubiquitin-proteasome system. Here we report the activities of SNIPER(ER) that targets estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) for degradation. SNIPER(ER) induced degradation of ERα and inhibited estrogen-dependent expression of pS2 gene in an estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell line MCF-7. A proteasome inhibitor MG132 and siRNA-mediated downregulation of cIAP1 abrogated the SNIPER(ER)-induced ERα degradation, suggesting that the ERα is degraded by proteasome subsequent to cIAP1-mediated ubiquitylation. Intriguingly, after the ERα degradation, the SNIPER(ER)-treated MCF-7 cells undergo rapid cell death. Detailed analysis indicated that SNIPER(ER) caused necrotic cell death accompanied by a release of HMGB1, a marker of necrosis, from the cells. Following the ERα degradation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) was produced in the SNIPER(ER)-treated MCF-7 cells, and an anti-oxidant N-acetylcysteine inhibited the necrotic cell death. These results indicate that SNIPER(ER) induces ERα degradation, ROS production and necrotic cell death, implying a therapeutic potential of SNIPER(ER) as a lead for the treatment of ERα-positive breast cancers.
© 2013 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Morales AR, Ganjei‐Azar P, Gomez‐Fernandez C, Nadji M. Immunohistochemistry of estrogen and progesterone receptors reconsidered. Am J Clin Path 2005; 123: 21–7. - PubMed
-
- Hall JM, McDonnell DP. Coregulators in nuclear estrogen receptor action: from concept to therapeutic targeting. Mol Interv 2005; 5: 343–57. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski AM, Pike AC, Dauter Z et al Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 1997; 389: 753–8. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein L, Deapen D, Cerhan JR et al Tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer and endometrial cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999; 91: 1654–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

