ReaChR: a red-shifted variant of channelrhodopsin enables deep transcranial optogenetic excitation
- PMID: 23995068
- PMCID: PMC3793847
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3502
ReaChR: a red-shifted variant of channelrhodopsin enables deep transcranial optogenetic excitation
Abstract
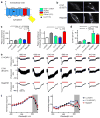
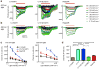
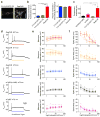
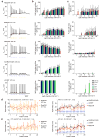
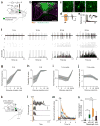
Channelrhodopsins (ChRs) are used to optogenetically depolarize neurons. We engineered a variant of ChR, denoted red-activatable ChR (ReaChR), that is optimally excited with orange to red light (λ ∼590-630 nm) and offers improved membrane trafficking, higher photocurrents and faster kinetics compared to existing red-shifted ChRs. Red light is less scattered by tissue and is absorbed less by blood than the blue to green wavelengths that are required by other ChR variants. We used ReaChR expressed in the vibrissa motor cortex to drive spiking and vibrissa motion in awake mice when excited with red light through intact skull. Precise vibrissa movements were evoked by expressing ReaChR in the facial motor nucleus in the brainstem and illumination with red light through the external auditory canal. Thus, ReaChR enables transcranial optical activation of neurons in deep brain structures without the need to surgically thin the skull, form a transcranial window or implant optical fibers.
Figures

References
-
- Arrenberg AB, Stainier DY, Baier H, Huisken J. Optogenetic control of cardiac function. Science. 2010;330:971–974. - PubMed
-
- Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Bruegmann T, et al. Optogenetic control of heart muscle in vitro and in vivo. Nat Methods. 2010;7:897–900. - PubMed
-
- Nagel G, et al. Channelrhodopsin-1: a light-gated proton channel in green algae. Science. 2002;296:2395–2398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- NS058668/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD006831/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058668/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059867/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 EB003832/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS027177/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 NS082097/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS027177/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS027177/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DA029706/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- OD006831/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA029706/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

