Oxidation-specific epitopes as targets for biotheranostic applications in humans: biomarkers, molecular imaging and therapeutics
- PMID: 23995232
- PMCID: PMC4085330
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328364e85a
Oxidation-specific epitopes as targets for biotheranostic applications in humans: biomarkers, molecular imaging and therapeutics
Abstract
Purpose of review: Emerging data demonstrate the potential of translational applications of antibodies directed against oxidation-specific epitopes (OSEs). 'Biotheranostics' as used in this context in cardiovascular disease (CVD) describes targeting of OSEs for biomarker, therapeutic and molecular imaging diagnostic applications.
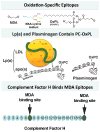
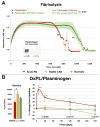
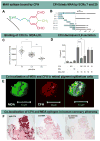
Recent findings: Atherogenesis can be viewed as a chronic, maladaptive inflammatory response to OSE and related antigens. Lipid oxidation collectively yields a large variety of OSE, such as oxidized phospholipids (OxPL) and malondialdehyde epitopes. OSEs are immunogenic, proinflammatory, proatherogenic and plaque destabilizing and represent danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). DAMPs are recognized by the innate immune system via pattern recognition receptors, including scavenger receptors, IgM natural antibodies and complement factor H, which bind, neutralize and/or facilitate their clearance. Biomarker assays measuring OxPL present on apolipoprotein B-100 lipoproteins, and particularly on lipoprotein (a), predict the development of CVD events. In contrast, OxPL on plasminogen facilitate fibrinolysis and may reduce atherothrombosis. Oxidation-specific antibodies attached to magnetic nanoparticles image lipid-rich, oxidation-rich plaques. Infusion or overexpression of oxidation-specific antibodies reduces the progression of atherosclerosis by potentially neutralizing and clearing OSE and preventing foam cell formation, suggesting similar applications in humans.
Summary: Using the accelerating knowledge base and improved understanding of the interplay of oxidation, inflammation and innate and adaptive immunity in atherogenesis, emerging clinical applications of oxidation-specific antibodies may identify, monitor and treat CVD in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Steinberg D, Parthasarathy S, Carew TE, et al. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:915–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

