Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR
- PMID: 23995387
- PMCID: PMC4118677
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2633
Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR
Abstract
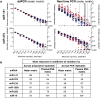
Nanoliter-sized droplet technology paired with digital PCR (ddPCR) holds promise for highly precise, absolute nucleic acid quantification. Our comparison of microRNA quantification by ddPCR and real-time PCR revealed greater precision (coefficients of variation decreased 37-86%) and improved day-to-day reproducibility (by a factor of seven) of ddPCR but with comparable sensitivity. When we applied ddPCR to serum microRNA biomarker analysis, this translated to superior diagnostic performance for identifying individuals with cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Sykes PJ, et al. Biotechniques. 1992;13:444–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

