Topiramate for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults
- PMID: 23996081
- PMCID: PMC8406931
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008314.pub3
Topiramate for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults
Abstract
Background: Topiramate is an antiepileptic drug with multiple possible mechanisms of action. Antiepileptic drugs are widely used to treat chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage) and fibromyalgia, and many guidelines recommend them.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and associated adverse events of topiramate for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults (aged 18 years and above).
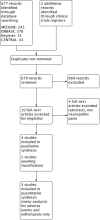
Search methods: On 8 May 2013, we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group Specialized Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE. We reviewed the bibliographies of all randomised trials identified and review articles, and also searched two clinical trial databases, ClinicalTrials.gov and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, to identify additional published or unpublished data.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) with double-blind assessment of participant outcomes following two weeks of treatment or longer (though the emphasis of the review was on studies of eight weeks or longer) that used a placebo or active comparator.
Data collection and analysis: We extracted efficacy and adverse event data, and two study authors examined issues of study quality independently. We performed analysis using two tiers of evidence. The first tier used data where studies reported the outcome of at least 50% pain reduction from baseline, lasted at least eight weeks, had a parallel group design, included 200 or more participants in the comparison, and reported an intention-to-treat analysis. First tier studies did not use last-observation-carried-forward (LOCF) or other imputation methods for dropouts. The second tier used data that failed to meet this standard; second tier results were therefore subject to potential bias.
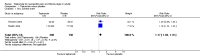
Main results: We included four studies with 1684 participants. Three parallel-group placebo comparisons were in painful diabetic neuropathy (1643 participants), and one cross-over study with diphenhydramine as an active placebo (41 participants) was in lumbar radiculopathy. Doses of topiramate were titrated up to 200 mg/day or 400 mg/day. All studies had one or more sources of potential major bias, as they either used LOCF imputation or were of small size.No study provided first tier evidence for an efficacy outcome. There was no convincing evidence for efficacy of topiramate at 200 to 400 mg/day over placebo.Eighty-two per cent of participants taking topiramate 200 to 400 mg/day experienced at least one adverse event, as did 71% with placebo, and the number needed to treat for an additional harmful effect (NNTH) was 8.6 (95% confidence interval (CI) 4.9 to 35). There was no difference in serious adverse events recorded (6.6% versus 7.5%). Adverse event withdrawals with 400 mg daily were much more common with topiramate (27%) than with placebo (8%), with an NNTH of 5.4 (95% CI 4.3 to 7.1). Lack of efficacy withdrawal was less frequent with topiramate (12%) than placebo (18%). Weight loss was a common event in most studies. No deaths attributable to treatment were reported.
Authors' conclusions: Topiramate is without evidence of efficacy in diabetic neuropathic pain, the only neuropathic condition in which it has been adequately tested. The data we have includes the likelihood of major bias due to LOCF imputation, where adverse event withdrawals are much higher with active treatment than placebo control. Despite the strong potential for bias, no difference in efficacy between topiramate and placebo was apparent.
Conflict of interest statement
SD and PW have received research support from charities, government, and industry sources at various times, but none relate to this review.
RAM has consulted for various pharmaceutical companies and received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies related to analgesics and other healthcare interventions, including (in the past five years) AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Company, Flynn Pharma, Furtura Medical, Grünenthal, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Horizon Pharma, Lundbeck, Menarini, MSD, Pfizer, Reckitt Benckiser, Sanofi Aventis, Urgo, Astellas, and Vifor Pharma.
MPL has received honoraria for consultation from Baxter Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring, and LfB, and he has received a travel support grant from Grifols. He has no interests to declare related to this review.
Figures





Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008314.pub2
References
References to studies included in this review
Khoromi 2005 {published data only}
NCT00231673 {published data only}
-
- Freeman R. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group study to evaluate the effect of topiramate on electrophysiologic parameters in subjects with diabetic peripheral polyneuropathy. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=NCT00231673 (accessed 9 May 2013).
Raskin 2004 {published data only}
Thienel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Thienel U, Neto W, Schwabe SK, Vijapurkar U, Topiramate Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Study Group. Topiramate in painful diabetic polyneuropathy: findings from three double‐blind placebo‐controlled trials. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2004;110(4):221‐31. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2004.00338.x; PUBMED: 15355485] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Edwards 1998 {published data only}
-
- Edwards KR, Glantz MJ, Levin P. An evaluation of topiramate in the management of painful diabetic neuropathy. American Pain Society 17th Annual Scientific Meeting, San Diego November 5‐8. 1998.
Edwards 2000 {published data only}
-
- Edwards KR, Glantz MJ, Button J, Norton JA, Whittaker T, Cross N. Efficacy and safety of topiramate in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Neurology. 2000; Vol. 54 (Suppl 3):A81.
Muehlbacher 2006 {published data only}
Vinik 2003 {published data only}
-
- Vinik A, Hewitt D, Xiang J, Jordan D, Rosenthal N. Topiramate in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: results from a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology. 2003; Vol. 60 (Suppl 1):A154‐5.
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT00001725 {published data only}
-
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR). Studies of dextromethorphan and topiramate to treat oral and facial pain. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00001725 2002 (accessed 9 May 2013).
Additional references
Antel 2012
Apkarian 2011
Attal 2010
Birse 2012
Bouhassira 2008
Carroll 2004
-
- Carroll DG, Kline KM, Malnar KF. Role of topiramate for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pharmacotherapy 2004;24(9):1186‐93. - PubMed
Chong 2003
-
- Chong MS, Libretto SE. The rationale and use of topiramate for treating neuropathic pain. The Clinical Journal of Pain 2003;19(1):59‐68. - PubMed
Chronicle 2004
Corrigan 2012
Derry 2012
Derry 2013
Donofrio 2005
-
- Donofrio PD, Raskin P, Rosenthal NR, Hewitt DJ, Jordan DM, Xiang J, et al (CAPSS‐141 Study Group). Safety and effectiveness of topiramate for the management of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in an open‐label extension study. Clinical Therapeutics 2005;27(9):1420‐31. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.09.011] - DOI - PubMed
Dworkin 2008
Gill 2011
Green 2012
Gustorff 2008
Gutierrez‐Alvarez 2007
Hall 2008
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. [PUBMED: 8721797] - PubMed
Jensen 2011
Jette 2008
Kanda 1996
-
- Kanda T, Kurokawa M, Tamura S, Nakamura J, Ishii A, Kuwana Y, et al. Topiramate reduces abnormally high extracellular levels of glutamate and aspartate in the hippocampus of spontaneously epileptic rats (SER). Life Sciences 1996;59(19):1607‐16. [PUBMED: 8913326] - PubMed
Katusic 1991
-
- Katusic S, Williams DB, Beard CM, Bergstralh EJ, Kurland LT. Epidemiology and clinical features of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: similarities and differences, Rochester, Minnesota,1945‐1984. Neuroepidemiology 1991;10(5‐6):276‐81. - PubMed
Khaliq 2007
Koopman 2009
Koroschetz 2011
L'Abbé 1987
-
- L'Abbé KA, Detsky AS, O'Rourke K. Meta‐analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107(2):224‐33. - PubMed
Lunn 2009
McNally 2006
-
- McNally JD, Matheson DA, Bakowsky VS. The epidemiology of self‐reported fibromyalgia in Canada. Chronic Diseases in Canada 2006;27(1):9‐16. - PubMed
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay H, Moore R. An Evidence‐Based Resource for Pain Relief. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263048‐2]
McQuay 2007
-
- McQuay HJ, Smith LA, Moore RA. Chronic Pain. In: Stevens A, Raftery J, Mant J, Simpson S editor(s). Health Care Needs Assessment: The Epidemiologically Based Needs Assessment Reviews: Third Series. Oxford: Radcliffe Publishing Ltd, 2007. [ISBN: 978‐1‐84619‐063‐6]
Moisset 2007
Moore 1998
-
- Moore RA, Gavaghan D, Tramèr MR, Collins SL, McQuay HJ. Size is everything ‐ large amounts of information are needed to overcome random effects in estimating direction and magnitude of treatment effects. Pain 1998;78(3):209‐16. [PUBMED: 9870574] - PubMed
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. Seattle: IASP Press, 2008:15‐24. [ISBN: 978–0–931092–69–5]
Moore 2009
Moore 2010a
-
- Moore RA, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. "Evidence" in chronic pain ‐ establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. [PUBMED: 20627575] - PubMed
Moore 2010b
Moore 2010c
Moore 2010d
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta‐analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374‐9. [DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.107805] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2011
Moore 2011a
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Paine J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Minimum efficacy criteria for comparisons between treatments using individual patient meta‐analysis of acute pain trials: examples of etoricoxib, paracetamol, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen/paracetamol combinations after third molar extraction. Pain 2011;152(5):982‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.030] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2011b
Moore 2012a
Moore 2012b
Moore 2013
Moore 2014
O'Brien 2010
O'Connor 2009
PaPaS 2011
-
- Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Group (PaPaS). PaPaS author and referee guidance. http://papas.cochrane.org/papas‐documents (accessed 22 January 2013).
Rappaport 1994
-
- Rappaport ZH, Devor M. Trigeminal neuralgia: the role of self‐sustaining discharge in the trigeminal ganglion. Pain 1994;56(2):127‐38. [PUBMED: 8008402 ] - PubMed
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Snedecor 2014
Soni 2013
Straube 2008
-
- Straube S, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Enriched enrollment: definition and effects of enrichment and dose in trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain. A systematic review. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008;66(2):266‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03200.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Straube 2010
Sultan 2008
Sun 2006
Torrance 2006
Tracey 2011
Treede 2008
Vos 2012
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2163‐96. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Walia 2004
-
- Walia KS, Khan EA, Ko DH, Raza SS, Khan YN. Side effects of antiepileptics ‐ a review. Pain Practice 2004;4(3):194‐203. [PUBMED: 17173601] - PubMed
Wiffen 2010
Wiffen 2011a
Wiffen 2011b
Wolfe 1990
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1990;33(2):160‐72. [PUBMED: 2306288] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

