Helical membrane protein conformations and their environment
- PMID: 23996195
- PMCID: PMC3818118
- DOI: 10.1007/s00249-013-0925-x
Helical membrane protein conformations and their environment
Abstract
Evidence that membrane proteins respond conformationally and functionally to their environment is growing. Structural models, by necessity, have been characterized in preparations where the protein has been removed from its native environment. Different structural methods have used various membrane mimetics that have recently included lipid bilayers as a more native-like environment. Structural tools applied to lipid bilayer-embedded integral proteins are informing us about important generic characteristics of how membrane proteins respond to the lipid environment as compared with their response to other nonlipid environments. Here, we review the current status of the field, with specific reference to observations of some well-studied α-helical membrane proteins, as a starting point to aid the development of possible generic principles for model refinement.
Figures
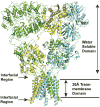



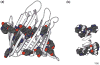


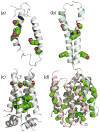
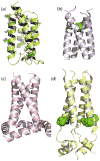





References
-
- Acharya R, Carnevale V, Fiorin G, Levine BG, Polishchuk AL, Balannik V, Samish I, Lamb RA, Pinto LH, DeGrado WF, Klein ML. Structure and mechanism of proton transport through the transmembrane tetrameric M2 protein bundle of the influenza A virus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(34):15075–15080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007071107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agre P. The aquaporins: Blueprints tor cellular plumbing systems. Faseb J. 1999;13(7):A1520–A1520. - PubMed
-
- Anfinsen CB. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science. 1973;181(96):223–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

