Gene targeting in mice: a review
- PMID: 23996268
- PMCID: PMC4524968
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-601-6_23
Gene targeting in mice: a review
Abstract
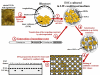
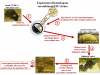
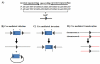
The ability to introduce DNA sequences (e.g., genes) of interest into the germline genome has rendered the mouse a powerful and indispensable experimental model in fundamental and medical research. The DNA sequences can be integrated into the genome randomly or into a specific locus by homologous recombination, in order to: (1) delete or insert mutations into genes of interest to determine their function, (2) introduce human genes into the genome of mice to generate animal models enabling study of human-specific genes and diseases, e.g., mice susceptible to infections by human-specific pathogens of interest, (3) introduce individual genes or genomes of pathogens (such as viruses) in order to examine the contributions of such genes to the pathogenesis of the parent pathogens, (4) and last but not least introduce reporter genes that allow monitoring in vivo or ex vivo the expression of genes of interest. Furthermore, the use of recombination systems, such as Cre/loxP or FRT/FLP, enables conditional induction or suppression of gene expression of interest in a restricted period of mouse's lifetime, in a particular cell type, or in a specific tissue. In this review, we will give an updated summary of the gene targeting technology and discuss some important considerations in the design of gene-targeted mice.
Figures



References
-
- Bot A, Casares S, Bot S, von Boehmer H, Bona C. Cellular mechanisms involved in protection against influenza virus infection in transgenic mice expressing a TCR receptor specific for class II hemagglutinin peptide in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1998;160:4500–4507. - PubMed
-
- Oxenius A, Bachmann MF, Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H. Virus-specific MHC-class II-restricted TCR-transgenic mice: effects on humoral and cellular immune responses after viral infection. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:390–400. - PubMed
-
- Pircher H, Burki K, Lang R, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel RM. Tolerance induction in double specific T-cell receptor transgenic mice varies with antigen. Nature. 1989;342:559–561. - PubMed
-
- Rall GF, Lawrence DM, Patterson CE. The application of transgenic and knockout mouse technology for the study of viral pathogenesis. Virology. 2000;271:220–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

