Bortezomib before and after autologous stem cell transplantation overcomes the negative prognostic impact of renal impairment in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a subgroup analysis from the HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 trial
- PMID: 23996482
- PMCID: PMC4007933
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.087585
Bortezomib before and after autologous stem cell transplantation overcomes the negative prognostic impact of renal impairment in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a subgroup analysis from the HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 trial
Abstract
Renal impairment is frequent in patients with multiple myeloma and is correlated with an inferior prognosis. This analysis evaluates the prognostic role of renal impairment in patients with myeloma treated with bortezomib before and after autologous stem cell transplantation within a prospective randomized phase III trial. Eight hundred and twenty-seven newly diagnosed myeloma patients in the HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 trial were randomized to receive three cycles of vincristine, adriamycin, dexamethasone (VAD) or bortezomib, adriamycin, dexamethasone (PAD) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation and maintenance with thalidomide 50 mg daily (VAD-arm) or bortezomib 1.3 mg/m(2) every 2 weeks (PAD-arm). Baseline serum creatinine was less than 2 mg/dL (Durie-Salmon-stage A) in 746 patients and 2 mg/dL or higher (stage B) in 81. In myeloma patients with a baseline creatinine ≥ 2 mg/dL the renal response rate was 63% in the VAD-arm and 81% in the PAD-arm (P=0.31). The overall myeloma response rate was 64% in the VAD-arm versus 89% in the PAD-arm with 13% complete responses in the VAD-arm versus 36% in the PAD-arm (P=0.01). Overall survival at 3 years for patients with a baseline creatinine ≥ 2 mg/dL was 34% in the VAD-arm versus 74% in the PAD-arm (P<0.001) with a progression-free survival rate at 3 years of 16% in the VAD-arm versus 48% in the PAD-arm (P=0.004). Overall and progression-free survival rates in the PAD-arm were similar in patients with a baseline creatinine ≥ 2 mg/dL or <2 mg/dL. We conclude that a bortezomib-containing treatment before and after autologous stem cell transplantation overcomes the negative prognostic impact of renal impairment in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. The trial was registered at www.trialregister.nl as NTR213 and at www.controlled-trials.com as ISRCTN 64455289.
Figures
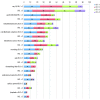
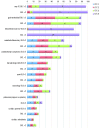
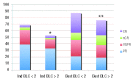

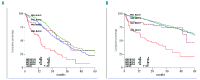
Comment in
-
Bortezomib just for induction or also for maintenance in myeloma patients with renal impairment?Haematologica. 2014 Jan;99(1):5-6. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.100982. Haematologica. 2014. PMID: 24425688 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Terpos E. Renal insufficiency and failure Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2010:431–6 - PubMed
-
- Knudsen LM, Hippe E, Hjorth M, Holmberg E, Westin J. Renal function in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma–a demographic study of 1353 patients. The Nordic Myeloma Study Group. Eur J Haematol. 1994;53(4):207–12 - PubMed
-
- Salmon SE, Durie BG. Cellular kinetics in multiple myeloma. A new approach to staging and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1975;135(1):131–8 - PubMed
-
- Greipp PR, San Miguel J, Durie BGM, Crowley J, Barlogie B, Blade J, et al. International Staging System for multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(15):3412–20 - PubMed
-
- Jagannath S, Barlogie B, Berenson JR, Singhal S, Alexanian R, Srkalovic G, et al. Bortezomib in recurrent and/or refractory multiple myeloma. Cancer. 2005;103(6):1195–200 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

