Doppler US in rheumatic diseases with special emphasis on rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 23996840
- PMCID: PMC4463240
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2013.13127
Doppler US in rheumatic diseases with special emphasis on rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis
Abstract
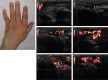
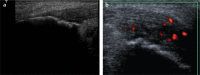
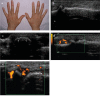
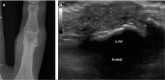
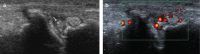
Developments in digital ultrasonography (US) technology and the use of high-frequency broadband transducers have increased the quality of US imaging, particularly of superficial tissues. Thus, US, particularly color US or power Doppler US, in which high-resolution transducers are used, has become an important imaging modality in the assessment of rheumatic diseases. Furthermore, therapeutic interventions and biopsies can be performed under US guidance during the assessment of lesions. In this era of effective treatments, such as biologics, improvements in synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis as well as changes in enthesitis in spondyloarthropathies, including ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis, can be monitored effectively using gray-scale and/or power Doppler US. US is also a good imaging modality for crystal arthropathies, including gout and pseudogout, in which synovitis, erosions, tophi, and crystal deposition within or around the joint can be visualized readily. Vascular and tenosynovial structures, as well as the salivary glands, can be assessed with US in vasculitis and connective tissue disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome. Current research is focused on improving the sensitivity, specificity, validity, and reproducibility of US findings. In this review, we summarized the role of US, particularly power Doppler US, in rheumatic diseases and inflammation in superficial tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Ribbens C, Andre B, Marcelis S, et al. Rheumatoid hand joint synovitis: gray-scale and power Doppler US quantifications following anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment: pilot study. Radiology. 2003;229:562–569. - PubMed
-
- Wakefield RJ, Gibbon WW, Conaghan PG, et al. The value of sonography in the detection of bone erosions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with conventional radiography. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2762–2770. - PubMed
-
- Wakefield RJ, Balint PV, Szkudlarek M, et al. Musculoskeletal ultrasound including definitions for ultrasonographic pathology. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:2485–2487. - PubMed
-
- Brown AK. Using ultrasonography to facilitate best practice in diagnosis and management of RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5:698–706. - PubMed
-
- Walther M, Harms H, Krenn V, Radke S, Faehndrich TP, Gohlke F. Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:331–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

