Vig r 6, the cytokinin-specific binding protein from mung bean (Vigna radiata) sprouts, cross-reacts with Bet v 1-related allergens and binds IgE from birch pollen allergic patients' sera
- PMID: 23996905
- PMCID: PMC4135424
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201300153
Vig r 6, the cytokinin-specific binding protein from mung bean (Vigna radiata) sprouts, cross-reacts with Bet v 1-related allergens and binds IgE from birch pollen allergic patients' sera
Abstract
Scope: Birch pollen associated allergy to mung bean sprouts is caused by cross-reactivity between the birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 and the mung bean allergen Vig r 1. We aimed to determine the allergenicity of the cytokinin-specific binding protein from mung bean (Vig r 6), another allergen related to Bet v 1 with only 31% sequence identity.
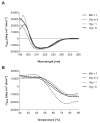
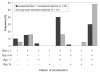
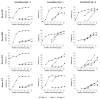
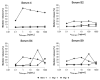
Methods and results: Bet v 1, Gly m 4, Vig r 1, and Vig r 6 were produced in Escherichia coli. In an ELISA, 73 and 32% of Bet v 1-sensitized birch-allergic patients' sera (n = 60) showed IgE binding to Vig r 1 and Vig r 6, respectively. Of 19 patients who reported allergic reactions or had positive prick-to-prick tests to mung bean sprouts, 79% showed IgE binding to Vig r 1 and 63% showed IgE binding to Vig r 6. Bet v 1 completely inhibited IgE binding to both mung bean allergens. Vig r 6 showed partial cross-reactivity with Vig r 1 and activated basophils sensitized with mung bean allergic patients' sera.
Conclusion: We demonstrated IgE cross-reactivity despite low sequence identity between Vig r 6 and other Bet v 1-related allergens. Thus, IgE binding to Vig r 6 may contribute to birch pollinosis-associated mung bean sprout allergy.
Keywords: Bet v 1; CSBP; Food allergy; IgE cross-reactivity; Vig r 6.
© 2013 The Authors. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chimeras of Bet v 1 and Api g 1 reveal heterogeneous IgE responses in patients with birch pollen allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Jul;134(1):188-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.12.1073. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24529686 Free PMC article.
-
High correlation of specific IgE sensitization between birch pollen, soy and apple allergens indicates pollen-food allergy syndrome among birch pollen allergic patients in northern China.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016 May;17(5):399-404. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500279. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016. PMID: 27143268 Free PMC article.
-
Birch pollen-related food allergy to legumes: identification and characterization of the Bet v 1 homologue in mungbean (Vigna radiata), Vig r 1.Clin Exp Allergy. 2005 Aug;35(8):1049-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02309.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16120087
-
Tree pollen allergens-an update from a molecular perspective.Allergy. 2015 Oct;70(10):1201-11. doi: 10.1111/all.12696. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Allergy. 2015. PMID: 26186076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand Binding of PR-10 Proteins with a Particular Focus on the Bet v 1 Allergen Family.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020 May 19;20(7):25. doi: 10.1007/s11882-020-00918-4. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020. PMID: 32430735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular approach to a patient's tailored diagnosis of the oral allergy syndrome.Clin Transl Allergy. 2020 Jun 17;10:22. doi: 10.1186/s13601-020-00329-8. eCollection 2020. Clin Transl Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32551040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filling the Antibody Pipeline in Allergy: PIPE Cloning of IgE, IgG1 and IgG4 against the Major Birch Pollen Allergen Bet v 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 8;21(16):5693. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165693. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784509 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the toxicological effects and allergenic potential of emerging alternative protein sources.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 Jan;24(1):e70123. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70123. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 39865634 Free PMC article.
-
The History and Science of the Major Birch Pollen Allergen Bet v 1.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 19;13(7):1151. doi: 10.3390/biom13071151. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic screening and detection of allergen cross-reactive IgE-binding epitopes.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017 Aug;61(8):1600676. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600676. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017. PMID: 28191711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Amato G, Spieksma FT, Liccardi G, Jager S, et al. Pollen-related allergy in Europe. Allergy. 1998;53:567–578. - PubMed
-
- Moverare R, Westritschnig K, Svensson M, Hayek B, et al. Different IgE reactivity profiles in birch pollen-sensitive patients from six European populations revealed by recombinant allergens: an imprint of local sensitization. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002;128:325–335. - PubMed
-
- Radauer C, Breiteneder H. Evolutionary biology of plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007;120:518–525. - PubMed
-
- Vieths S, Scheurer S, Ballmer-Weber B. Current understanding of cross-reactivity of food allergens and pollen. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2002;964:47–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

