Imatinib attenuates monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension and has potent vasodilator activity in pulmonary and systemic vascular beds in the rat
- PMID: 23997103
- PMCID: PMC3840242
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00329.2013
Imatinib attenuates monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension and has potent vasodilator activity in pulmonary and systemic vascular beds in the rat
Abstract
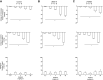
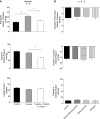
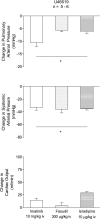
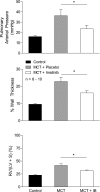
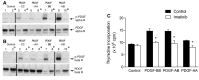
Cardiovascular responses to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib were investigated in the rat. Intravenous injections of 0.3-30 mg/kg imatinib produced small decreases in pulmonary arterial pressure, larger dose-dependent decreases in systemic arterial pressure, and no change or small increases in cardiac output, suggesting that the systemic vasodilator response is more pronounced under baseline conditions. When pulmonary arterial pressure was increased with U-46619 or N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), intravenous injections of imatinib produced larger dose-dependent decreases in pulmonary arterial pressure. Imatinib attenuated the acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstrictor response. Vasodilator responses to imatinib were not inhibited by meclofenamate, glybenclamide, or rolipram, suggesting that cyclooxygenase, ATP-sensitive K(+) (KATP) channels, and cAMP were not involved in mediating the response. In a 21-day prevention study, imatinib treatment (50 mg/kg ip) attenuated the increase in pulmonary arterial pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy, and small vessel remodeling induced by monocrotaline. Imatinib reduced PDGF receptor phosphorylation and PDGF-stimulated thymidine incorporation in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. These data suggest that the beneficial effect of imatinib in pulmonary hypertension may involve inhibition of PDGF tyrosine kinase receptor-mediated effects on smooth muscle cell proliferation and on vasoconstrictor tone. These results indicate that imatinib has nonselective vasodilator activity in the pulmonary and systemic vascular beds similar to the Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil and the calcium entry antagonist isradipine. The present results are consistent with the hypothesis that imatinib may inhibit a constitutively active tyrosine kinase vasoconstrictor pathway in the pulmonary and systemic vascular beds in the rat.
Keywords: PDGF; imatinib; pulmonary vascular bed; tyrosine kinase inhibitor; vasodilation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of responses to the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 in the pulmonary and systemic vascular bed of the rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):H184-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00181.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20435851 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are potent acute pulmonary vasodilators in rats.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Oct;45(4):804-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0371OC. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21378262 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Src tyrosine kinases in experimental pulmonary hypertension.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Jun;32(6):1354-65. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.248500. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22516066
-
Evaluation of imatinib mesylate in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Future Cardiol. 2010 Jan;6(1):19-35. doi: 10.2217/fca.09.54. Future Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20014985 Review.
-
[Treatment with imatinib for refractory PAH].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2014 Apr;143(4):173-7. doi: 10.1254/fpj.143.173. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 24717604 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of Akt1, but not Akt2, attenuates the development of pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;308(2):L208-20. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00242.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25416384 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for Old and New Small-Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors as Effective Treatments in Pulmonary Hypertension-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 29;25(23):12858. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312858. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684570 Free PMC article.
-
Sildenefil increases connexin 40 in smooth muscle cells through activation of BMP pathways in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jul 15;7(8):4674-84. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25197339 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors relax pulmonary arteries in human and murine precision-cut lung slices.Respir Res. 2019 Jun 6;20(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1074-2. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31170998 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled tyrosine kinase inhibitors for pulmonary hypertension: a possible future treatment.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Oct 7;8:1753-63. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S70277. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25336919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badejo AM, Jr, Dhaliwal JS, Casey DB, Gallen TB, Greco AJ, Kadowitz PJ. Analysis of pulmonary vasodilator responses to the Rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil in the anesthetized rat. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295: L828–L836, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Biers SM, Reynard JM, Doore T, Brading AF. The functional effects of a c-kit tyrosine inhibitor on guinea-pig and human detrusor. BJU Int 97: 612–616, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Carroll M, Ohno-Jones S, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Lydon NB, Gilliland DG, Druker BJ. CGP 57148, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits the growth of cells expressing BCR-ABL, TEL-ABL, and TEL-PDGFR fusion proteins. Blood 90: 4947–4952, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

