Genome-wide RNAi high-throughput screen identifies proteins necessary for the AHR-dependent induction of CYP1A1 by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- PMID: 23997114
- PMCID: PMC3829574
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kft191
Genome-wide RNAi high-throughput screen identifies proteins necessary for the AHR-dependent induction of CYP1A1 by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
Abstract
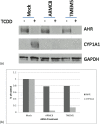
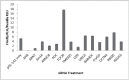
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) has a plethora of physiological roles, and upon dysregulation, carcinogenesis can occur. One target gene of AHR encodes the xenobiotic and drug-metabolizing enzyme CYP1A1, which is inducible by the environmental contaminant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) via the AHR. An siRNA library targeted against over 5600 gene candidates in the druggable genome was used to transfect mouse Hepa-1 cells, which were then treated with TCDD, and subsequently assayed for CYP1A1-dependent ethoxyresorufin-o-deethylase (EROD) activity. Following redundant siRNA activity (RSA) statistical analysis, we identified 93 hits that reduced EROD activity with a p value ≤ .005 and substantiated 39 of these as positive hits in a secondary screening using endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs (esiRNAs). Twelve of the corresponding gene products were subsequently confirmed to be necessary for the induction of CYP1A1 messenger RNA by TCDD. None of the candidates were deficient in aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator expression. However 6 gene products including UBE2i, RAB40C, CRYGD, DCTN4, RBM5, and RAD50 are required for the expression of AHR as well as for induction of CYP1A1. We also found 2 gene products, ARMC8 and TCF20, to be required for the induction of CYP1A1, but our data are ambiguous as to whether they are required for the expression of AHR. In contrast, SIN3A, PDC, TMEM5, and CD9 are not required for AHR expression but are required for the induction of CYP1A1, implicating a direct role in Cyp1a1 transcription. Our methods, although applied to Cyp1a1, could be modified for identifying proteins that regulate other inducible genes.
Keywords: AHR; CYP1A1; RNAi; TCDD; esiRNA.; high-throughput screening.
Figures






Similar articles
-
SIN3A, generally regarded as a transcriptional repressor, is required for induction of gene transcription by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 28;289(48):33655-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.611236. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25305016 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of a chloracne phenotype in an epidermal equivalent model by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is dependent on aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and is not reproduced by aryl hydrocarbon receptor knock down.J Dermatol Sci. 2014 Jan;73(1):10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Dermatol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24161567 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia perturbs aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and CYP1A1 expression induced by PCB 126 in human skin and liver-derived cell lines.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 1;274(3):408-16. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24355420 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Feb 17;1619(3):263-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00485-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12573486 Review.
-
Role of coactivators in transcriptional activation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 15;433(2):379-86. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.031. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581594 Review.
Cited by
-
A CRISPR/Cas9 Whole-Genome Screen Identifies Genes Required for Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Dependent Induction of Functional CYP1A1.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Aug 1;170(2):310-319. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz111. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31086989 Free PMC article.
-
A model for aryl hydrocarbon receptor-activated gene expression shows potency and efficacy changes and predicts squelching due to competition for transcription co-activators.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 3;10(6):e0127952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127952. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26039703 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation is globally disrupted and associated with expression changes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease small airways.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 May;50(5):912-22. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0304OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24298892 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Suppressive Functions of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) and AhR as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer.Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;12(4):526. doi: 10.3390/biology12040526. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ah Receptor Pathway Intricacies; Signaling Through Diverse Protein Partners and DNA-Motifs.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015 Sep 1;4(5):1143-1158. doi: 10.1039/c4tx00236a. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 26783425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akabane H., Fan J., Zheng X., Zhu G. Z. (2007). Protein kinase C activity in mouse eggs regulates gamete membrane interaction. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 74, 1465–1472 - PubMed
-
- Beischlag T. V., Wang S., Rose D. W., Torchia J., Reisz-Porszasz S., Muhammad K., Nelson W. E., Probst M. R., Rosenfeld M. G., Hankinson O. (2002). Recruitment of the NCoA/SRC-1/p160 family of transcriptional coactivators by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 4319–4333 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

