The design and optimization of RNA trans-splicing molecules for skin cancer therapy
- PMID: 23998959
- PMCID: PMC5528447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.08.005
The design and optimization of RNA trans-splicing molecules for skin cancer therapy
Abstract
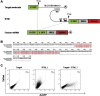
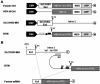
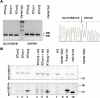
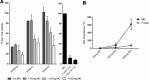
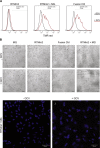
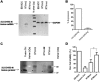
Targeting tumor marker genes by RNA trans-splicing is a promising means to induce tumor cell-specific death. Using a screening system we designed RNA trans-splicing molecules (RTM) specifically binding the pre-mRNA of SLCO1B3, a marker gene in epidermolysis bullosa associated squamous cell carcinoma (EB-SCC). Specific trans-splicing, results in the fusion of the endogenous target mRNA of SLCO1B3 and the coding sequence of the suicide gene, provided by the RTM. SLCO1B3-specific RTMs containing HSV-tk were analyzed regarding their trans-splicing potential in a heterologous context using a SLCO1B3 expressing minigene (SLCO1B3-MG). Expression of the chimeric SLCO1B3-tk was detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Cell viability and apoptosis assays confirmed that the RTMs induced suicide gene-mediated apoptosis in SLCO1B3-MG expressing cells. The lead RTM also showed its potential to facilitate a trans-splicing reaction into the endogenous SLCO1B3 pre-mRNA in EB-SCC cells resulting in tk-mediated apoptosis. We assume that the pre-selection of RTMs by our inducible cell-death system accelerates the design of optimal RTMs capable to induce tumor specific cell death in skin cancer cells.
Keywords: 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; BD; BP; Cancer gene therapy; DT-A; EB; EB-SCC; Epidermolysis bullosa; GAPDH; GCV; GCVTP; HSV; Herpes simplex virus – thymidine kinase (HSV-tk); IRES; MG; MMP9; MTT; PPT; RDEB; RNA trans-splicing; RNA trans-splicing molecule; RTM; RTM mutated 1, RTM mutated 2; RTM original; RTMm1, RTMm2; RTMmut; RTMorg; SCC; SLCO1B3; SMaRT; SS; STS; SqRT-PCR; Squamous cell carcinoma; TUNEL; binding domain; branch point; diphtheria toxin subunit A; epidermolysis bullosa; epidermolysis bullosa-associated squamous cell carcinoma; ganciclovir; ganciclovir triphosphate; glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; herpes simplex virus; internal ribosomal entry site; matrix metalloproteinase 9; minigene; poly pyrimidine tract; recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; segmental trans-splicing; semi-quantitative real time PCR; solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B3; splice site; spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing; splicing deficient RTM; squamous cell carcinoma; terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; thymidine kinase; tk; β-subunit of human gonadotropin gene 6; βhCG6.
Copyright © 2013 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Altaner, C. , 2008. Prodrug cancer gene therapy. Cancer Lett.. 270, 191–201. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, J.W. , Murauer, E.M. , Wally, V. , Koller, U. , 2013. RNA trans-splicing for genodermatoses. Methods Mol. Biol.. 961, 441–455. - PubMed
-
- Chao, H. , Mansfield, S.G. , Bartel, R.C. , Hiriyanna, S. , Mitchell, L.G. , Garcia-Blanco, M.A. , Walsh, C.E. , 2003. Phenotype correction of hemophilia A mice by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Nat. Med.. 9, 1015–1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

