Normalization and extraction of interpretable metrics from raw accelerometry data
- PMID: 23999141
- PMCID: PMC4072911
- DOI: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxt029
Normalization and extraction of interpretable metrics from raw accelerometry data
Abstract
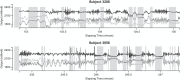
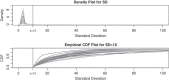
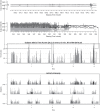
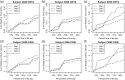
We introduce an explicit set of metrics for human activity based on high-density acceleration recordings from a hip-worn tri-axial accelerometer. These metrics are based on two concepts: (i) Time Active, a measure of the length of time when activity is distinguishable from rest and (ii) AI, a measure of the relative amplitude of activity relative to rest. All measurements are normalized (have the same interpretation across subjects and days), easy to explain and implement, and reproducible across platforms and software implementations. Metrics were validated by visual inspection of results and quantitative in-lab replication studies, and by an association study with health outcomes.
Keywords: Activity intensity; Movelets; Movement; Signal processing; Time active; Tri-axial accelerometer.
Figures

References
-
- ActiGraph. What are counts. 2013. https//help.theactigraph.com/entries/-What-are-counts- (accessed 26 April)
-
- Ancoli-Israel S., Cole R., Alessi C., Chambers M., Moorcroft W., Pollak C. The role of actigraphy in the study of sleep and circadian rhythms. American academy of sleep medicine review paper. Sleep. 2003;26(3):342–392. - PubMed
-
- Bai J. Accelerometer-based prediction of activity for epidemiological research, [Master’s Thesis] 2011 Johns Hopkins University.
-
- Bao L., Intille S. S. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Pervasive Computing. Berlin: Springe; 2004. Activity recognition from user-annotated acceleration data; pp. 1–17. Linz/Vienna, Austria, 21–23 April 2004.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

