Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of rivaroxaban
- PMID: 23999929
- PMCID: PMC3889701
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-013-0100-7
Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of rivaroxaban
Abstract
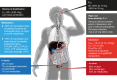
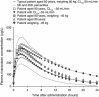
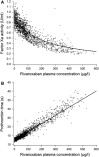
Rivaroxaban is an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor that targets free and clot-bound Factor Xa and Factor Xa in the prothrombinase complex. It is absorbed rapidly, with maximum plasma concentrations being reached 2-4 h after tablet intake. Oral bioavailability is high (80-100 %) for the 10 mg tablet irrespective of food intake and for the 15 mg and 20 mg tablets when taken with food. Variability in the pharmacokinetic parameters is moderate (coefficient of variation 30-40 %). The pharmacokinetic profile of rivaroxaban is consistent in healthy subjects and across a broad range of different patient populations studied. Elimination of rivaroxaban from plasma occurs with a terminal half-life of 5-9 h in healthy young subjects and 11-13 h in elderly subjects. Rivaroxaban produces a pharmacodynamic effect that is closely correlated with its plasma concentration. The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic relationship for inhibition of Factor Xa activity can be described by an E max model, and prothrombin time prolongation by a linear model. Rivaroxaban does not inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes or known drug transporter systems and, because rivaroxaban has multiple elimination pathways, it has no clinically relevant interactions with most commonly prescribed medications. Rivaroxaban has been approved for clinical use in several thromboembolic disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Bayer Pharma AG. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) Summary of Product Characteristics; 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info... (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
-
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) Prescribing Information; 2013. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/022406s004lbl.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

