Are skeletal muscle FNDC5 gene expression and irisin release regulated by exercise and related to health?
- PMID: 24000180
- PMCID: PMC3936375
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.263707
Are skeletal muscle FNDC5 gene expression and irisin release regulated by exercise and related to health?
Abstract
Recently, contradictory findings have been reported concerning the function of irisin and its precursor gene, skeletal muscle FNDC5, in energy homeostasis, and the associated regulatory role of exercise and PGC-1α. We therefore evaluated whether muscle FNDC5 mRNA and serum irisin are exercise responsive and whether PGC-1α expression is associated with FNDC5 expression. The male subjects in the study performed single exercises: (1) 1 h low-intensity aerobic exercise (AE) (middle-aged, n = 17), (2) a heavy-intensity resistance exercise (RE) bout (young n = 10, older n = 11) (27 vs. 62 years), (3) long-term 21 weeks endurance exercise (EE) training alone (twice a week, middle-aged, n = 9), or (4) combined EE and RE training (both twice a week, middle-aged, n = 9). Skeletal muscle mRNA expression was analysed by quantitative PCR and serum irisin by ELISA. No significant changes were observed in skeletal muscle PGC-1α, FNDC5 and serum irisin after AE, EE training or combined EE + RE training. However, a single RE bout increased PGC-1α by 4-fold in young and by 2-fold in older men, while FNDC5 mRNA only increased in young men post-RE, by 1.4-fold. Changes in PGC-1α or serum irisin were not consistently accompanied by changes in FNDC5. In conclusion, for the most part, neither longer-term nor single exercise markedly increases skeletal muscle FNDC5 expression or serum irisin. Therefore their changes in response to exercise are probably random and not consistent excluding the confirmation of any definitive link between exercise and FNDC5 expression and irisin release in humans. Moreover, irisin and FNDC5 were not associated with glucose tolerance and being overweight, or with metabolic disturbances, respectively. Finally, factor(s) other than PGC-1α and transcription may regulate FNDC5 expression.
Figures

 ) aerobic exercise (AE) performed with bicycle ergometry (n= 17); 21 weeks endurance training (EE, n= 9); combined endurance + resistance training (EE + RE, n= 9), and in age-matched non-exercised controls (Con, n= 2). In A, B and C the error bars represent mean values and the whiskers are 95% confidence intervals. The circles represent individual values. D, individual responses to exercise. Each line represents one individual and links the change of PGC-1α to the change of FNDC5 mRNA after exercise. E, individual responses to exercise. Each line represents one individual and links the change of FNDC5 mRNA to the change of serum irisin after exercise. (Data are pooled from panels A and B.) F, serum irisin concentrations (ng ml−1) before and after AE. G, serum irisin concentrations (ng ml−1) before and after EE and combined EE + RE. H, serum irisin concentrations after 1, 15 and 30 min of a heavy-exercise bout.
) aerobic exercise (AE) performed with bicycle ergometry (n= 17); 21 weeks endurance training (EE, n= 9); combined endurance + resistance training (EE + RE, n= 9), and in age-matched non-exercised controls (Con, n= 2). In A, B and C the error bars represent mean values and the whiskers are 95% confidence intervals. The circles represent individual values. D, individual responses to exercise. Each line represents one individual and links the change of PGC-1α to the change of FNDC5 mRNA after exercise. E, individual responses to exercise. Each line represents one individual and links the change of FNDC5 mRNA to the change of serum irisin after exercise. (Data are pooled from panels A and B.) F, serum irisin concentrations (ng ml−1) before and after AE. G, serum irisin concentrations (ng ml−1) before and after EE and combined EE + RE. H, serum irisin concentrations after 1, 15 and 30 min of a heavy-exercise bout.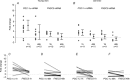
Comment in
-
Greek goddess or Greek myth: the effects of exercise on irisin/FNDC5 in humans.J Physiol. 2013 Nov 1;591(21):5267-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.265371. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24187077 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The effects of acute and chronic exercise on PGC-1α, irisin and browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(3):739-49. doi: 10.1111/febs.12619. Epub 2013 Dec 10. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24237962 Clinical Trial.
-
SMAD3 negatively regulates serum irisin and skeletal muscle FNDC5 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1-α (PGC-1α) during exercise.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 20;290(12):7671-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617399. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25648888 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Dependent Changes in Increased Levels of Plasma Irisin and Muscle PGC-1α and FNDC5 after Exercise in Mice.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018 Feb;244(2):93-103. doi: 10.1620/tjem.244.93. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29415899
-
From Skeletal Muscle to Myocardium: Molecular Mechanisms of Exercise-Induced Irisin Regulation of Cardiac Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 10;26(8):3550. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083550. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of irisin in physiology and pathology.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 26;13:962968. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.962968. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36225200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of circulating irisin levels with normal weight obesity, glycemic and lipid profile.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016 Jun 27;15:17. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0239-5. eCollection 2015. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 27354972 Free PMC article.
-
The Acute Effects of Swimming Exercise on PGC-1α-FNDC5/Irisin-UCP1 Expression in Male C57BL/6J Mice.Metabolites. 2021 Feb 16;11(2):111. doi: 10.3390/metabo11020111. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33669194 Free PMC article.
-
Change of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Level Correlates with the Severity of Diabetic Sensory Polyneuropathy after Six-Week Physical Activity.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 28;23(5):160. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2305160. eCollection 2022 May. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39077619 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Pubertal Stage on the Concentrations of the Novel Adipomyokine, Irisin, in Male Adolescents.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020 Jun 3;12(2):168-174. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0119. Epub 2019 Sep 13. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31514491 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin a Novel Metabolic Biomarker: Present Knowledge and Future Directions.Int J Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 9;2018:7816806. doi: 10.1155/2018/7816806. eCollection 2018. Int J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30402097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahtiainen JP, Hulmi JJ, Kraemer WJ, Lehti M, Pakarinen A, Mero AA, Karavirta L, Sillanpaa E, Selanne H, Alen M, Komulainen J, Kovanen V, Nyman K, Hakkinen K. Strength [corrected], endurance or combined training elicit diverse skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain isoform proportion but unaltered androgen receptor concentration in older men. Int J Sports Med. 2009;30:879–887. - PubMed
-
- Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Boström EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, Kajimura S, Zingaretti MC, Vind BF, Tu H, Cinti S, Højlund K, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481:463–468. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V, Brinkoetter M, Vamvini MT, Schneider BE, Mantzoros CS. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism. 2012;61:1725–1738. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hulmi JJ, Kovanen V, Lisko I, Selanne H, Mero AA. The effects of whey protein on myostatin and cell cycle-related gene expression responses to a single heavy resistance exercise bout in trained older men. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008;102:205–213. - PubMed
-
- Hulmi JJ, Kovanen V, Selänne H, Kraemer WJ, Häkkinen K, Mero AA. Acute and long-term effects of resistance exercise with or without protein ingestion on muscle hypertrophy and gene expression. Amino Acids. 2009a;37:297–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

