Computational analysis of the binding specificity of Gleevec to Abl, c-Kit, Lck, and c-Src tyrosine kinases
- PMID: 24001034
- PMCID: PMC4026022
- DOI: 10.1021/ja405939x
Computational analysis of the binding specificity of Gleevec to Abl, c-Kit, Lck, and c-Src tyrosine kinases
Abstract
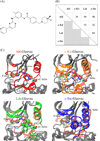
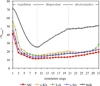
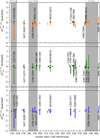
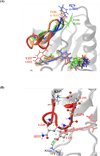
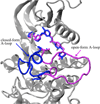
Gleevec, a well-known cancer therapeutic agent, is an effective inhibitor of several tyrosine kinases, including Abl and c-Kit, but displays less potency to inhibit closely homologous tyrosine kinases, such as Lck and c-Src. Because many structural features of the binding site are highly conserved in these homologous kinases, the molecular determinants responsible for the binding specificity of Gleevec remain poorly understood. To address this issue, free energy perturbation molecular dynamics (FEP/MD) simulations with explicit solvent was used to compute the binding affinity of Gleevec to Abl, c-Kit, Lck, and c-Src. The results of the FEP/MD calculations are in good agreement with experiments, enabling a detailed and quantitative dissection of the absolute binding free energy in terms of various thermodynamic contributions affecting the binding specificity of Gleevec to the kinases. Dominant binding free energy contributions arises from the van der Waals dispersive interaction, compensating about two-thirds of the unfavorable free energy penalty associated with the loss of translational, rotational, and conformational freedom of the ligand upon binding. In contrast, the contributions from electrostatic and repulsive interactions nearly cancel out due to solvent effects. Furthermore, the calculations show the importance of the conformation of the kinase activation loop. Among the kinases examined, Abl provides the most favorable binding environment for Gleevec via optimal protein-ligand interactions and a small free energy cost for loss of the translational, rotational, and conformational freedom upon ligand binding. The FEP/MD calculations additionally reveal that Lck and c-Src provide similar nonbinding interactions with the bound-Gleevec, but the former pays less entropic penalty for the ligand losing its translational, rotational, and conformational motions to bind, examining the empirically observed differential binding affinities of Gleevec between the two Src-family kinases.
Figures

References
-
- Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Mett H, Meyer T, Muller M, Druker BJ, Lydon NB. Cancer Res. 1996;56:100. - PubMed
-
- Lydon N. Nat. Med. 2009;15:1153. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S, Zimmermann J, Lydon NB. Nat. Med. 1996;2:561. - PubMed
-
- Sawyers CL, Hochhaus A, Feldman E, Goldman JM, Miller CB, Ottmann OG, Schiffer CA, Talpaz M, Guilhot F, Deininger MW, Fischer T, O'Brien SG, Stone RM, Gambacorti-Passerini CB, Russell NH, Reiffers JJ, Shea TC, Chapuis B, Coutre S, Tura S, Morra E, Larson RA, Saven A, Peschel C, Gratwohl A, Mandelli F, Ben-Am M, Gathmann I, Capdeville R, Paquette RL, Druker BJ. Blood. 2002;99:3530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

