Drug screening in Scn1a zebrafish mutant identifies clemizole as a potential Dravet syndrome treatment
- PMID: 24002024
- PMCID: PMC3891590
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3410
Drug screening in Scn1a zebrafish mutant identifies clemizole as a potential Dravet syndrome treatment
Abstract
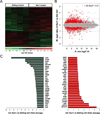
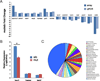
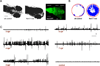
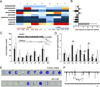
Dravet syndrome is a catastrophic pediatric epilepsy with severe intellectual disability, impaired social development and persistent drug-resistant seizures. One of its primary monogenic causes are mutations in Nav1.1 (SCN1A), a voltage-gated sodium channel. Here we characterize zebrafish Nav1.1 (scn1Lab) mutants originally identified in a chemical mutagenesis screen. Mutants exhibit spontaneous abnormal electrographic activity, hyperactivity and convulsive behaviours. Although scn1Lab expression is reduced, microarray analysis is remarkable for the small fraction of differentially expressed genes (~3%) and lack of compensatory expression changes in other scn subunits. Ketogenic diet, diazepam, valproate, potassium bromide and stiripentol attenuate mutant seizure activity; seven other antiepileptic drugs have no effect. A phenotype-based screen of 320 compounds identifies a US Food and Drug Administration-approved compound (clemizole) that inhibits convulsive behaviours and electrographic seizures. This approach represents a new direction in modelling pediatric epilepsy and could be used to identify novel therapeutics for any monogenic epilepsy disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Harkin LA, et al. The spectrum of SCN1A-related infantile epileptic encephalopathies. Brain. 2007;130:843–852. - PubMed
-
- Mulley JC, et al. SCN1A mutations and epilepsy. Hum. Mutat. 2005;25:535–542. - PubMed
-
- Ceulemans BP, Claes LR, Lagae LG. Clinical correlations of mutations in the SCN1A gene: from febrile seizures to severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy. Pediatric Neurol. 2004;30:236–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

