Generalized bacterial genome editing using mobile group II introns and Cre-lox
- PMID: 24002656
- PMCID: PMC3792343
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2013.41
Generalized bacterial genome editing using mobile group II introns and Cre-lox
Abstract
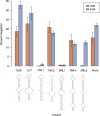
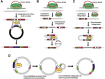
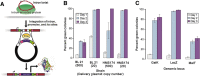
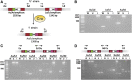
Efficient bacterial genetic engineering approaches with broad-host applicability are rare. We combine two systems, mobile group II introns ('targetrons') and Cre/lox, which function efficiently in many different organisms, into a versatile platform we call GETR (Genome Editing via Targetrons and Recombinases). The introns deliver lox sites to specific genomic loci, enabling genomic manipulations. Efficiency is enhanced by adding flexibility to the RNA hairpins formed by the lox sites. We use the system for insertions, deletions, inversions, and one-step cut-and-paste operations. We demonstrate insertion of a 12-kb polyketide synthase operon into the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli, multiple simultaneous and sequential deletions of up to 120 kb in E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus, inversions of up to 1.2 Mb in E. coli and Bacillus subtilis, and one-step cut-and-pastes for translocating 120 kb of genomic sequence to a site 1.5 Mb away. We also demonstrate the simultaneous delivery of lox sites into multiple loci in the Shewanella oneidensis genome. No selectable markers need to be placed in the genome, and the efficiency of Cre-mediated manipulations typically approaches 100%.
Conflict of interest statement
Targetron technology is subject to issued US and foreign patents and patent applications that are licensed by the Ohio State University and the University of Texas to InGex, LLC, which sublicenses the technology to others for commercial applications. JP, AML, the Ohio State University, and the University of Texas are minority equity holders in InGex, LLC, and AML serves as an advisor to InGex, LLC. JP and AML may receive royalty payments for commercial use of the technology. JP is the founder of a company, Targetronics, which sublicenses targetron technology from InGex, LLC.
Figures


References
-
- Albert H, Dale EC, Lee E, Ow DW (1995) Site-specific integration of DNA into wild-type and mutant lox sites placed in the plant genome. Plant J 7: 649–659 - PubMed
-
- Beloin C, Deighan P, Doyle M, Dorman CJ (2003) Shigella flexneri 2a strain 2457T expresses three members of the H-NS-like protein family: characterization of the Sfh protein. Mol Genet Genomics 270: 66–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

