Novel hybrid GPU-CPU implementation of parallelized Monte Carlo parametric expectation maximization estimation method for population pharmacokinetic data analysis
- PMID: 24002801
- PMCID: PMC3787213
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-013-9524-0
Novel hybrid GPU-CPU implementation of parallelized Monte Carlo parametric expectation maximization estimation method for population pharmacokinetic data analysis
Abstract
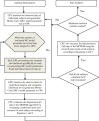
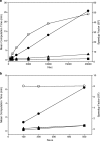
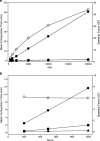
The development of a population PK/PD model, an essential component for model-based drug development, is both time- and labor-intensive. A graphical-processing unit (GPU) computing technology has been proposed and used to accelerate many scientific computations. The objective of this study was to develop a hybrid GPU-CPU implementation of parallelized Monte Carlo parametric expectation maximization (MCPEM) estimation algorithm for population PK data analysis. A hybrid GPU-CPU implementation of the MCPEM algorithm (MCPEMGPU) and identical algorithm that is designed for the single CPU (MCPEMCPU) were developed using MATLAB in a single computer equipped with dual Xeon 6-Core E5690 CPU and a NVIDIA Tesla C2070 GPU parallel computing card that contained 448 stream processors. Two different PK models with rich/sparse sampling design schemes were used to simulate population data in assessing the performance of MCPEMCPU and MCPEMGPU. Results were analyzed by comparing the parameter estimation and model computation times. Speedup factor was used to assess the relative benefit of parallelized MCPEMGPU over MCPEMCPU in shortening model computation time. The MCPEMGPU consistently achieved shorter computation time than the MCPEMCPU and can offer more than 48-fold speedup using a single GPU card. The novel hybrid GPU-CPU implementation of parallelized MCPEM algorithm developed in this study holds a great promise in serving as the core for the next-generation of modeling software for population PK/PD analysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High performance computing for deformable image registration: towards a new paradigm in adaptive radiotherapy.Med Phys. 2008 Aug;35(8):3546-53. doi: 10.1118/1.2948318. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 18777915
-
Large-scale neural circuit mapping data analysis accelerated with the graphical processing unit (GPU).J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Jan 15;239:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.09.022. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 25277633 Free PMC article.
-
Parallelized computation for computer simulation of electrocardiograms using personal computers with multi-core CPU and general-purpose GPU.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2010 Oct;100(1):87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2010.06.015. Epub 2010 Jul 31. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2010. PMID: 20674066
-
Graphics Processing Unit-Enhanced Genetic Algorithms for Solving the Temporal Dynamics of Gene Regulatory Networks.Evol Bioinform Online. 2018 Apr 10;14:1176934318767889. doi: 10.1177/1176934318767889. eCollection 2018. Evol Bioinform Online. 2018. PMID: 29662297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GPU-based high-performance computing for radiation therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2014 Feb 21;59(4):R151-82. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/4/R151. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24486639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Remedial Dosing Recommendations for Sirolimus Delayed or Missed Dosages Caused by Poor Medication Compliance in Pediatric Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Patients.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(11):877-886. doi: 10.2174/0113816128299479240213151714. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38454763
References
-
- Davidian M, Giltinan DM. Nonlinear models for repeated measures data. New York: Chapman & Hall; 1995.
-
- Bauer RJ, Guzy S. Monte Carlo Parametric Expectation Maximization (MC-PEM) method for analyzing population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) data. In: D’ Argenio DZ, editor. Advanced Methods of Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic System Analysis. Boston: Kluwer; 2004. p. 135–63.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

