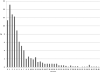
Distribution of National Institutes of Health stroke scale in the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study
- PMID: 24003048
- PMCID: PMC4632977
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.002881
Distribution of National Institutes of Health stroke scale in the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study
Abstract
Background and purpose: Little is known about the distribution of National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores from patients with ischemic stroke sampled from population-based studies. We describe the distribution of NIHSS in ischemic stroke cases from the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study.
Methods: Within a biracial population of 1.3 million, all strokes among area residents in 2005 were ascertained by screening discharge records at local hospitals and outpatient clinics. A sampling scheme was developed to ascertain additional cases presenting to physician offices and nursing homes, not identified through the other sources. All confirmed ischemic stroke cases underwent chart abstraction, and a retrospective NIHSS (rNIHSS) score (range, 0-42) was generated on the basis of initial physician examination findings.
Results: There were 2233 ischemic stroke cases identified during the 12-month study. The overall median rNIHSS score was 3 (interquartile range, 1-7). Median rNIHSS score was 3, 7, and 1, respectively, for stroke cases ascertained through the admitted, in-hospital, and out-of-hospital sources. Median rNIHSS was significantly higher in subjects ≥80 years compared with younger cases (4 versus 3).
Conclusions: More than half of all ischemic stroke cases have mild symptom severity on initial presentation (ie, rNIHSS≤3). Monitoring trends in NIHSS represents a legitimate target for population-based surveillance efforts.
Keywords: severity; stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Kasner SE. Clinical interpretation and use of stroke scales. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:603–612. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP, Jr., Davis PH, Leira EC, Chang KC, Bendixen BH, Clarke WR, et al. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: A report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology. 1999;53:126–131. - PubMed
-
- Smith EE, Shobha N, Dai D, Olson DM, Reeves MJ, Saver JL, et al. Risk score for in-hospital ischemic stroke mortality derived and validated within the Get With the Guidelines-Stroke Program. Circulation. 2010;122:1496–1504. - PubMed
-
- Kleindorfer DO, Khoury J, Moomaw CJ, Alwell K, Woo D, Flaherty ML, et al. Stroke incidence is decreasing in whites but not in blacks: a population-based estimate of temporal trends in stroke incidence from the Greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study. Stroke. 2010;41:1326–1331. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams LS, Yilmaz EY, Lopez-Yunez AM. Retrospective assessment of initial stroke severity with the NIH stroke scale. Stroke. 2000;31:858–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical