Murine Fig4 is dispensable for muscle development but required for muscle function
- PMID: 24004519
- PMCID: PMC3844516
- DOI: 10.1186/2044-5040-3-21
Murine Fig4 is dispensable for muscle development but required for muscle function
Abstract
Background: Phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs) are low-abundance phospholipids that participate in a range of cellular processes, including cell migration and membrane traffic. PIP levels and subcellular distribution are regulated by a series of lipid kinases and phosphatases. In skeletal muscle, PIPs and their enzymatic regulators serve critically important functions exemplified by mutations of the PIP phosphatase MTM1 in myotubular myopathy (MTM), a severe muscle disease characterized by impaired muscle structure and abnormal excitation-contraction coupling. FIG4 functions as a PIP phosphatase that participates in both the synthesis and breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PI(3,5)P2). Mutation of FIG4 results in a severe neurodegenerative disorder in mice and a progressive peripheral polyneuropathy in humans. The effect of FIG4 mutation on skeletal muscle has yet to be examined.
Methods: Herein we characterize the impact of FIG4 on skeletal muscle development and function using the spontaneously occurring mouse mutant pale tremor (plt), a mouse line with a loss of function mutation in Fig4.
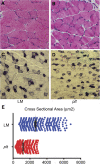
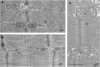
Results: In plt mice, we characterized abnormalities in skeletal muscle, including reduced muscle size and specific force generation. We also uncovered ultrastructural abnormalities and increased programmed cell death. Conversely, we detected no structural or functional abnormalities to suggest impairment of excitation-contraction coupling, a process previously shown to be influenced by PI(3,5)P2 levels. Conditional rescue of Fig4 mutation in neurons prevented overt muscle weakness and the development of obvious muscle abnormalities, suggesting that the changes observed in the plt mice were primarily related to denervation of skeletal muscle. On the basis of the ability of reduced FIG4 levels to rescue aspects of Mtmr2-dependent neuropathy, we evaluated the effect of Fig4 haploinsufficiency on the myopathy of Mtm1-knockout mice. Male mice with a compound Fig4+/-/Mtm1-/Y genotype displayed no improvements in muscle histology, muscle size or overall survival, indicating that FIG4 reduction does not ameliorate the Mtm1-knockout phenotype.
Conclusions: Overall, these data indicate that loss of Fig4 impairs skeletal muscle function but does not significantly affect its structural development.
Figures


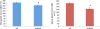


Similar articles
-
Protective role of the lipid phosphatase Fig4 in the adult nervous system.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Jul 15;27(14):2443-2453. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy145. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29688489 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous Administration of a MTMR2-Encoding AAV Vector Ameliorates the Phenotype of Myotubular Myopathy in Mice.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2018 Apr 1;77(4):282-295. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nly002. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29408998 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the neuropathy-associated MTMR2 gene rescues MTM1-associated myopathy.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Oct 1;26(19):3736-3748. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx258. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28934386
-
[Myotubular myopathy].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2000 Nov;156(11):960-4. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2000. PMID: 11119047 Review. French.
-
X-linked myotubular myopathy.Neuromuscul Disord. 2021 Oct;31(10):1004-1012. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2021.08.003. Neuromuscul Disord. 2021. PMID: 34736623 Review.
Cited by
-
FIG4 regulates lysosome membrane homeostasis independent of phosphatase function.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Feb 15;25(4):681-92. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv505. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 26662798 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3C2B inhibition improves function and prolongs survival in myotubular myopathy animal models.J Clin Invest. 2016 Sep 1;126(9):3613-25. doi: 10.1172/JCI86841. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27548528 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Genetic Background of Spastic Syndrome in North American Holstein Cattle Based on Heritability, Genome-Wide Association, and Functional Genomic Analyses.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 20;14(7):1479. doi: 10.3390/genes14071479. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510383 Free PMC article.
-
The Protein Complex of Neurodegeneration-related Phosphoinositide Phosphatase Sac3 and ArPIKfyve Binds the Lewy Body-associated Synphilin-1, Preventing Its Aggregation.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 20;290(47):28515-28529. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.669929. Epub 2015 Sep 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26405034 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of the lipid phosphatase Fig4 in the adult nervous system.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Jul 15;27(14):2443-2453. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy145. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29688489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zolov SN, Bridges D, Zhang Y, Lee WW, Riehle E, Verma R, Lenk GM, Converso-Baran K, Weide T, Albin RL, Saltiel AR, Meisler MH, Russell MW, Weisman LS. In vivo, Pikfyve generates PI(3,5)P2, which serves as both a signaling lipid and the major precursor for PI5P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:17472–17477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203106109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

