Paravertebral compartment syndrome after training causing severe back pain in an amateur rugby player: report of a rare case and review of the literature
- PMID: 24004522
- PMCID: PMC3848892
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-259
Paravertebral compartment syndrome after training causing severe back pain in an amateur rugby player: report of a rare case and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Acute compartment syndrome (CS) of the paravertebral muscles without external trauma is rarely reported in literature. Not all of clinical symptoms for CS are applicable to the paravertebral region.
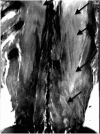
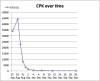
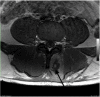
Case presentation: A 30-year-old amateur rugby player was suffering from increasing back pain following exertional training specially targeting back muscles. He presented with hardly treatable pain of the lumbar spine, dysaesthesia of the left paravertebral lumbar region as well as elevated muscle enzymes. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed an edema of the paravertebral muscles. Compartment pressure measurement revealed increased values of 47 mmHg on the left side. Seventy-two hours after onset of back pain a fasciotomy of the superficial thoracolumbar fascia was performed. Immediately postoperatively the clinical condition improved and enzyme levels significantly decreased. The patient started with light training exercises 3 weeks after the operation.
Conclusions: We present a rare case of an exercise-induced compartment syndrome of the paravertebral muscles and set it in the context of existing literature comparing various treatment options and outcomes. Where there is evidence of paravertebral compartment syndrome we recommend immediate fasciotomy to prevent rhabdomyolysis and further consequential diseases.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

