Changes in calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor component and nitric oxide receptor (sGC) immunoreactivity in rat trigeminal ganglion following glyceroltrinitrate pretreatment
- PMID: 24004534
- PMCID: PMC3847895
- DOI: 10.1186/1129-2377-14-74
Changes in calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor component and nitric oxide receptor (sGC) immunoreactivity in rat trigeminal ganglion following glyceroltrinitrate pretreatment
Abstract
Background: Nitric oxide (NO) is thought to play an important role in the pathophysiology of migraine. Infusion of the nitrovasodilator glyceroltrinitrate (nitroglycerin, GTN), which mobilizes NO in the organism, is an approved migraine model in humans. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is regarded as another key mediator in migraine. Increased plasma levels of CGRP have been found during spontaneous as well as nitrovasodilator-induced migraine attacks. The nociceptive processes and interactions underlying the NO and CGRP mediated headache are poorly known but can be examined in animal experiments. In the present study we examined changes in immunofluorescence of CGRP receptor components (CLR and RAMP1) and soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), the intracellular receptor for NO, in rat trigeminal ganglia after pretreatment with GTN.
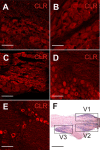
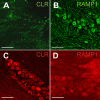
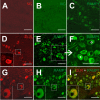
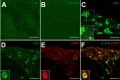
Methods: Isoflurane anaesthetised rats were intravenously infused with GTN (1 mg/kg) or saline for four hours and two hours later the trigeminal ganglia were processed for immunohistochemistry. Different primary antibodies recognizing CLR, RAMP1, CGRP and sGC coupled to fluorescent secondary antibodies were used to examine immunoreactive cells in serial sections of trigeminal ganglia with epifluorescence and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Several staining protocols were examined to yield optimized immunolabeling.
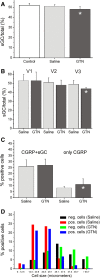
Results: In vehicle-treated animals, 42% of the trigeminal ganglion neurons were immunopositive for RAMP1 and 41% for CLR. After GTN pretreatment CLR-immunopositivity was unchanged, while there was an increase in RAMP1-immunopositive neurons to 46%. RAMP1 and CLR immunoreactivity was also detected in satellite cells. Neurons immunoreactive for sGC were on average smaller than sGC-immunonegative neurons. The percentage of sGC-immunopositive neurons (51% after vehicle) was decreased after GTN infusion (48%).
Conclusions: Prolonged infusion of GTN caused increased fractions of RAMP1- and decreased fractions of sGC-immunopositive neurons in the trigeminal ganglion. The observed alterations are likely immunophenotypic correlates of the pathophysiological processes underlying nitrovasodilator-induced migraine attacks and indicate that signalling via CGRP receptors but not sGC-mediated mechanisms may be enhanced through endogenous NO production.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR), receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactivity in the rat trigeminovascular system: differences between peripheral and central CGRP receptor distribution.J Comp Neurol. 2008 Mar 20;507(3):1277-99. doi: 10.1002/cne.21607. J Comp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18186028
-
Sex differences in behavior and expression of CGRP-related genes in a rodent model of chronic migraine.Headache. 2011 May;51(5):674-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01882.x. Headache. 2011. PMID: 21521205 Free PMC article.
-
Differential distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptor components in the human trigeminal ganglion.Neuroscience. 2010 Aug 25;169(2):683-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.05.016. Epub 2010 May 22. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20472035
-
The Trigeminovascular Pathway: Role of CGRP and CGRP Receptors in Migraine.Headache. 2017 May;57 Suppl 2:47-55. doi: 10.1111/head.13081. Headache. 2017. PMID: 28485848 Review.
-
Recognizing the role of CGRP and CGRP receptors in migraine and its treatment.Cephalalgia. 2019 Mar;39(3):366-373. doi: 10.1177/0333102417736900. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Cephalalgia. 2019. PMID: 29020807 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation of RAMP1 gene in migraine: an exploratory analysis.J Headache Pain. 2015;16:90. doi: 10.1186/s10194-015-0576-7. Epub 2015 Oct 26. J Headache Pain. 2015. PMID: 26501962 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Mediating both Excitatory and Inhibitory Effects in a Rat Model of Meningeal Nociception and Headache Generation.Front Neurol. 2017 Jul 14;8:336. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00336. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28769868 Free PMC article.
-
Is serum S100B protein an useful biomarker in migraine?Neurol Sci. 2014 Aug;35(8):1197-201. doi: 10.1007/s10072-014-1679-7. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24531979
-
Cross-talk signaling in the trigeminal ganglion: role of neuropeptides and other mediators.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020 Apr;127(4):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02161-7. Epub 2020 Feb 22. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020. PMID: 32088764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding of trigeminal ganglion structure and function in headache.Cephalalgia. 2019 Nov;39(13):1661-1674. doi: 10.1177/0333102418786261. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Cephalalgia. 2019. PMID: 29989427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Juhasz G, Zsombok T, Modos EA, Olajos S, Jakab B, Nemeth J, Szolcsanyi J, Vitrai J, Bagdy G. NO-induced migraine attack: strong increase in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) concentration and negative correlation with platelet serotonin release. Pain. 2003;14:461–470. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2003.09.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

