Small nucleolar RNAs as new biomarkers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 24004562
- PMCID: PMC3766210
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-6-27
Small nucleolar RNAs as new biomarkers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
Background: Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and small Cajal body-specific RNAs are non-coding RNAs involved in the maturation of other RNA molecules. Alterations of sno/scaRNA expression may play a role in cancerogenesis. This study elucidates the patterns of sno/scaRNA expression in 211 chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients (Binet stage A) also in comparison with those of different normal B-cell subsets.
Methods: The patterns of sno/scaRNA expression in highly purified CD19+ B-cells of 211 CLL patients and in 18 normal B-cell samples--6 from peripheral blood, and 12 from tonsils (4 germinal center, 2 marginal zone, 3 switched memory and 3 naïve B-cells)--were analyzed on the Affymetrix GeneChip® Human Gene 1.0 ST array.
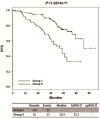
Results: CLLs display a sno/scaRNAs expression profile similar to normal memory, naïve and marginal-zone B-cells, with the exception of a few down-regulated transcripts (SNORA31, -6, -62, and -71C). Our analyses also suggest some heterogeneity in the pattern of sno/scaRNAs expression which is apparently unrelated to the major biological (ZAP-70 and CD38), molecular (IGHV mutation) and cytogenetic markers. Moreover, we found that SNORA70F was significantly down-regulated in poor prognostic subgroups and this phenomenon was associated with the down-regulation of its host gene COBLL1. Finally, we generated an independent model based on SNORA74A and SNORD116-18 expression, which appears to distinguish two different prognostic CLL groups.
Conclusions: These data extend the view of sno/scaRNAs deregulation in cancer and may contribute to discover novel biomarkers associated with the disease and potentially useful to predict the clinical outcome of early stage CLL patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The expression pattern of small nucleolar and small Cajal body-specific RNAs characterizes distinct molecular subtypes of multiple myeloma.Blood Cancer J. 2012 Nov 23;2(11):e96. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2012.41. Blood Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 23178508 Free PMC article.
-
Sno/scaRNAbase: a curated database for small nucleolar RNAs and cajal body-specific RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D183-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl873. Epub 2006 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17099227 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAome expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: comparison with normal B-cell subsets and correlations with prognostic and clinical parameters.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Aug 1;20(15):4141-53. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2497. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24916701
-
Biology and clinical relevance of noncoding sno/scaRNAs.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Feb;28(2):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 28869095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Clinical applications and prognostic markers.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2016 Mar;29(1):79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2016. PMID: 27742074 Review.
Cited by
-
Epitranscriptomics in Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 9;21(18):6578. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186578. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32916783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Cajal Body-Specific RNA12 Promotes Carcinogenesis through Modulating Extracellular Matrix Signaling in Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;16(3):483. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030483. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339238 Free PMC article.
-
Small nucleolar RNA is potential as a novel player in leukemogenesis and clinical application.Blood Sci. 2021 Oct 19;3(4):122-131. doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000091. eCollection 2021 Oct. Blood Sci. 2021. PMID: 35402848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Small Nucleolar RNAs in Cancers - An Evidence Map.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Apr 8;15:3851-3864. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S352333. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35431571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Promising Role of Non-Coding RNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Leukemia.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;14(1):131. doi: 10.3390/genes14010131. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

