Anti-diabetic treatment regulates pro-fibrotic TGF-β serum levels in type 2 diabetics
- PMID: 24004910
- PMCID: PMC3847073
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-48
Anti-diabetic treatment regulates pro-fibrotic TGF-β serum levels in type 2 diabetics
Abstract
Background: The single-center, open-label, four-arm, exploratory study investigates the relation of different anti-diabetics to serum levels of active TGF-β, a known pro-fibrotic stimulus, before and after a defined test meal.
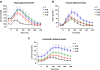
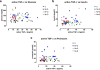
Findings: We investigated sera of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with metformin and sulfonylurea, insulin glargine or a DPP-4 inhibitor (DPP4i). Patients' sera were analyzed before and 5 h after a defined test meal at intervals of 30 min.The sulfonylurea/metformin group exhibited the highest basal levels of active TGF-β (31.50 ± 3.58 ng/ml). The glargine/metformin group had active TGF-β levels (24.98 ± 1.90 ng/ml) that were comparable to those of the healthy participants (22.12 ± 2.34 ng/ml). The lowest basal levels of active TGF-β were detected in the DPP-4i/metformin group (12.28 ± 0.84 ng/ml). Following the intake of a standardized meal, active TGF-β levels decreased (approx. 30%) in healthy subjects as well as in the sulfonylurea/metformin group and in the glargine/metformin group. After 5 h, the active TGF-β levels were normalized to basal levels. Active TGF-β levels in the DPP-4i/metformin group did not change significantly after the test meal. Overall plasma levels of insulin and proinsulin were comparable between healthy participants, and T2DM patients in the glargin/metformin group and in the DPP4i/metformin group. However, no correlation between active TGF-β levels, glucose, insulin or pro-insulin levels was detected.
Conclusions: T2DM patients often exhibit elevated levels of pro-fibrotic active TGF-β. Our results suggest that glargine/metformin and DPP4i/metformin treatment may more effectively reduce active TGF-β serum levels than the sulfonylurea/metformin treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of glargine insulin versus rosiglitazone addition in poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients on metformin plus sulfonylurea.Diabetes Care. 2006 Nov;29(11):2371-7. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0564. Diabetes Care. 2006. PMID: 17065670 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of linagliptin compared with glimepiride on postprandial glucose metabolism, islet cell function and vascular function parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving ongoing metformin treatment.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014 Oct;30(7):582-9. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2525. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014. PMID: 24459063 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily insulin glargine as add-on to metformin (with or without sulfonylureas) in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational, phase 3a trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017 May;5(5):355-366. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30085-2. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28344112 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012 Mar 1;51(3):147-62. doi: 10.2165/11598080-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012. PMID: 22339447 Review.
-
Second line therapy: type 2 diabetic subjects failing on metformin GLP-1/DPP-IV inhibitors versus sulphonylurea/insulin: for GLP-1/DPP-IV inhibitors.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012 Dec;28 Suppl 2:21-5. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2350. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 23280862 Review.
Cited by
-
Targets and candidate agents for type 2 diabetes treatment with computational bioinformatics approach.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:763936. doi: 10.1155/2014/763936. Epub 2014 Oct 21. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 25401107 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer: Effects on cancer tissue and novel perspectives.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jun;13(6):3975-3981. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6008. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28599404 Free PMC article.
-
Use of in vitro bone models to screen for altered bone metabolism, osteopathies, and fracture healing: challenges of complex models.Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):3937-3958. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02906-z. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32910238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal Regulation of Hepatic TGF-β1 and Foxo1 Controls Gluconeogenesis and Energy Expenditure.Diabetes. 2023 Sep 1;72(9):1193-1206. doi: 10.2337/db23-0180. Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37343276 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the protective effects of dichloroacetic acid in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 22;26(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00849-8. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39844306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koppel H, Riedl E, Braunagel M, Sauerhoefer S, Ehnert S, Godoy P, Sternik P, Dooley S, Yard BA. L-carnosine inhibits high-glucose-mediated matrix accumulation in human mesangial cells by interfering with TGF-beta production and signalling. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:3852–3858. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr324. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

