Protein tyrosine phosphatase α in the dorsomedial striatum promotes excessive ethanol-drinking behaviors
- PMID: 24005290
- PMCID: PMC3761047
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1954-13.2013
Protein tyrosine phosphatase α in the dorsomedial striatum promotes excessive ethanol-drinking behaviors
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2015 Dec 9;35(49):16295-6
Abstract
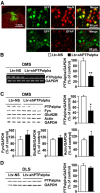
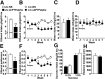
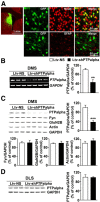
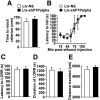
We previously found that excessive ethanol drinking activates Fyn in the dorsomedial striatum (DMS) (Wang et al., 2010; Gibb et al., 2011). Ethanol-mediated Fyn activation in the DMS leads to the phosphorylation of the GluN2B subunit of the NMDA receptor, to the enhancement of the channel's activity, and to the development and/or maintenance of ethanol drinking behaviors (Wang et al., 2007, 2010). Protein tyrosine phosphatase α (PTPα) is essential for Fyn kinase activation (Bhandari et al., 1998), and we showed that ethanol-mediated Fyn activation is facilitated by the recruitment of PTPα to synaptic membranes, the compartment where Fyn resides (Gibb et al., 2011). Here we tested the hypothesis that PTPα in the DMS is part of the Fyn/GluN2B pathway and is thus a major contributor to the neuroadaptations underlying excessive ethanol intake behaviors. We found that RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated PTPα knockdown in the DMS reduces excessive ethanol intake and preference in rodents. Importantly, no alterations in water, saccharine/sucrose, or quinine intake were observed. Furthermore, downregulation of PTPα in the DMS of mice significantly reduces ethanol-mediated Fyn activation, GluN2B phosphorylation, and ethanol withdrawal-induced long-term facilitation of NMDAR activity without altering the intrinsic features of DMS neurons. Together, these results position PTPα upstream of Fyn within the DMS and demonstrate the important contribution of the phosphatase to the maladaptive synaptic changes that lead to excessive ethanol intake.
Figures





References
-
- Ben Hamida S, Neasta J, Lasek AW, Kharazia V, Zou M, Carnicella S, Janak PH, Ron D. The small G protein H-Ras in the mesolimbic system is a molecular gateway to alcohol-seeking and excessive drinking behaviors. J Neurosci. 2012;32:15849–15858. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2846-12.2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
