Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates cocaine reinstatement through local and antidromic activation
- PMID: 24005296
- PMCID: PMC3761051
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4804-12.2013
Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates cocaine reinstatement through local and antidromic activation
Abstract
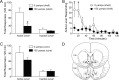
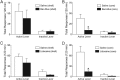
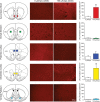
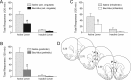
Accumbal deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a promising therapeutic modality for the treatment of addiction. Here, we demonstrate that DBS in the nucleus accumbens shell, but not the core, attenuates cocaine priming-induced reinstatement of drug seeking, an animal model of relapse, in male Sprague Dawley rats. Next, we compared DBS of the shell with pharmacological inactivation. Results indicated that inactivation using reagents that influenced (lidocaine) or spared (GABA receptor agonists) fibers of passage blocked cocaine reinstatement when administered into the core but not the shell. It seems unlikely, therefore, that intrashell DBS influences cocaine reinstatement by inactivating this nucleus or the fibers coursing through it. To examine potential circuit-wide changes, c-Fos immunohistochemistry was used to examine neuronal activation following DBS of the nucleus accumbens shell. Intrashell DBS increased c-Fos induction at the site of stimulation as well as in the infralimbic cortex, but had no effect on the dorsal striatum, prelimbic cortex, or ventral pallidum. Recent evidence indicates that accumbens DBS antidromically stimulates axon terminals, which ultimately activates GABAergic interneurons in cortical areas that send afferents to the shell. To test this hypothesis, GABA receptor agonists (baclofen/muscimol) were microinjected into the anterior cingulate, and prelimbic or infralimbic cortices before cocaine reinstatement. Pharmacological inactivation of all three medial prefrontal cortical subregions attenuated the reinstatement of cocaine seeking. These results are consistent with DBS of the accumbens shell attenuating cocaine reinstatement via local activation and/or activation of GABAergic interneurons in the medial prefrontal cortex via antidromic stimulation of cortico-accumbal afferents.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson SM, Schmidt HD, Pierce RC. Administration of the D2 dopamine receptor antagonist sulpiride into the shell, but not the core, of the nucleus accumbens attenuates cocaine priming-induced reinstatement of drug seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:1452–1461. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300922. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson SM, Bari AA, Pierce RC. Administration of the D1-like dopamine receptor antagonist SCH-23390 into the medial nucleus accumbens shell attenuates cocaine priming-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003;168:132–138. doi: 10.1007/s00213-002-1298-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benazzouz A, Hallett M. Mechanism of action of deep brain stimulation. Neurology. 2000;55(12 Suppl 6):S13–S16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
