Recombinant probes reveal dynamic localization of CaMKIIα within somata of cortical neurons
- PMID: 24005308
- PMCID: PMC3761057
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2108-13.2013
Recombinant probes reveal dynamic localization of CaMKIIα within somata of cortical neurons
Abstract
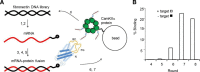
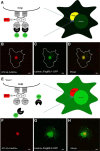
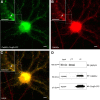
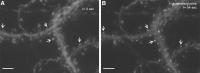
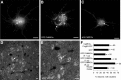
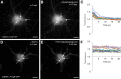
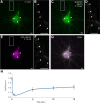
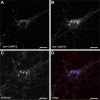
In response to NMDA receptor stimulation, CaMKIIα moves rapidly from a diffuse distribution within the shafts of neuronal dendrites to a clustered postsynaptic distribution. However, less is known about CaMKIIα localization and trafficking within neuronal somata. Here we use a novel recombinant probe capable of labeling endogenous CaMKIIα in living rat neurons to examine its localization and trafficking within the somata of cortical neurons. This probe, which was generated using an mRNA display selection, binds to endogenous CaMKIIα at high affinity and specificity following expression in rat cortical neurons in culture. In ∼45% of quiescent cortical neurons, labeled clusters of CaMKIIα 1-4 μm in diameter were present. Upon exposure to glutamate and glycine, CaMKIIα clusters disappeared in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner within seconds. Moreover, minutes after the removal of glutamate and glycine, the clusters returned to their original configuration. The clusters, which also appear in cortical neurons in sections taken from mouse brains, contain actin and disperse upon exposure to cytochalasin D, an actin depolymerizer. In conclusion, within the soma, CaMKII localizes and traffics in a manner that is distinct from its localization and trafficking within the dendrites.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
