HELQ promotes RAD51 paralogue-dependent repair to avert germ cell loss and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 24005329
- PMCID: PMC3836231
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12565
HELQ promotes RAD51 paralogue-dependent repair to avert germ cell loss and tumorigenesis
Abstract
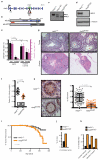
Repair of interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) requires the coordinated action of the intra-S-phase checkpoint and the Fanconi anaemia pathway, which promote ICL incision, translesion synthesis and homologous recombination (reviewed in refs 1, 2). Previous studies have implicated the 3'-5' superfamily 2 helicase HELQ in ICL repair in Drosophila melanogaster (MUS301 (ref. 3)) and Caenorhabditis elegans (HELQ-1 (ref. 4)). Although in vitro analysis suggests that HELQ preferentially unwinds synthetic replication fork substrates with 3' single-stranded DNA overhangs and also disrupts protein-DNA interactions while translocating along DNA, little is known regarding its functions in mammalian organisms. Here we report that HELQ helicase-deficient mice exhibit subfertility, germ cell attrition, ICL sensitivity and tumour predisposition, with Helq heterozygous mice exhibiting a similar, albeit less severe, phenotype than the null, indicative of haploinsufficiency. We establish that HELQ interacts directly with the RAD51 paralogue complex BCDX2 and functions in parallel to the Fanconi anaemia pathway to promote efficient homologous recombination at damaged replication forks. Thus, our results reveal a critical role for HELQ in replication-coupled DNA repair, germ cell maintenance and tumour suppression in mammals.
Figures



Comment in
-
DNA damage: Running in parallel.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Oct;13(10):679. doi: 10.1038/nrc3607. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24060858 No abstract available.
References
-
- Muzzini DM, Plevani P, Boulton SJ, Cassata G, Marini F. Caenorhabditis elegans POLQ-1 and HEL-308 function in two distinct DNA interstrand cross-link repair pathways. DNA Repair (Amst) 2008;7:941–950. - PubMed
Additional Methods References
-
- Horn C, et al. Splinkerette PCR for more efficient characterization of gene trap events. Nature Genet. 2007;39:933–934. - PubMed
-
- Dupuy AJ, Fritz S, Largaespada DA. Transposition and gene disruption in the male germline of the mouse. Genesis. 2001;30:82–88. - PubMed
-
- Truett GE, et al. Preparation of PCR-quality mouse genomic DNA with hot sodium hydroxide and tris (HotSHOT) BioTechniques. 2000;29:52, 54. - PubMed
-
- Kratz K, et al. Deficiency of FANCD2-associated nuclease KIAA1018/FAN1 sensitizes cells to interstrand crosslinking agents. Cell. 2010;142:77–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

