Radiation dose in neuroangiography using image noise reduction technology: a population study based on 614 patients
- PMID: 24005833
- PMCID: PMC3825538
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-013-1276-0
Radiation dose in neuroangiography using image noise reduction technology: a population study based on 614 patients
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to quantify the reduction in patient radiation dose by X-ray imaging technology using image noise reduction and system settings for neuroangiography and to assess its impact on the working habits of the physician.
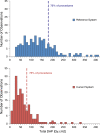
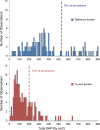
Methods: Radiation dose data from 190 neuroangiographies and 112 interventional neuroprocedures performed with state-of-the-art image processing and reference system settings were collected for the period January-June 2010. The system was then configured with extra image noise reduction algorithms and system settings, which enabled radiation dose reduction without loss of image quality. Radiation dose data from 174 neuroangiographies and 138 interventional neuroprocedures were collected for the period January-June 2012. Procedures were classified as diagnostic or interventional. Patient radiation exposure was quantified using cumulative dose area product and cumulative air kerma. Impact on working habits of the physician was quantified using fluoroscopy time and number of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images.
Results: The optimized system settings provided significant reduction in dose indicators versus reference system settings (p<0.001): from 124 to 47 Gy cm(2) and from 0.78 to 0.27 Gy for neuroangiography, and from 328 to 109 Gy cm(2) and from 2.71 to 0.89 Gy for interventional neuroradiology. Differences were not significant between the two systems with regard to fluoroscopy time or number of DSA images.
Conclusion: X-ray imaging technology using an image noise reduction algorithm and system settings provided approximately 60% radiation dose reduction in neuroangiography and interventional neuroradiology, without affecting the working habits of the physician.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart FA, Akleyev AV, Hauer-Jensen M, Hendry JH, Kleiman NJ, MacVittie TJ, Aleman BM, Edgar AB, Mabuchi K, Muirhead CR, Shore RE, Wallace WH. ICRP Publication 118: ICRP statement on tissue reactions and early and late effects of radiation in normal tissues and organs — threshold doses for tissue reactions in a radiation protection context. Ann ICRP. 2012;41(1–2):1–322. doi: 10.1016/j.icrp.2012.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Söderman M, Holmin S, Andersson T, Palmgren C, Babić D, Hoornaert B. Clinical results with an image noise reduction algorithm for digital subtraction angiography. Radiology. 2013 - PubMed
-
- Miller DL, Balter S, Cole PE, Lu HT, Schueler BA, Geisinger M, Berenstein A, Albert R, Georgia JD, Noonan PT, Cardella JF, St George J, Russell EJ, Malisch TW, Vogelzang RL, Miller GL, 3rd, Anderson J. Radiation doses in interventional radiology procedures: the RAD-IR study: Part I. Overall measures of dose. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003;14:711–727. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000079980.80153.4B. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

