Heart genetics in a small package, exploiting the condensed genome of Ciona intestinalis
- PMID: 24005910
- PMCID: PMC3896895
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elt034
Heart genetics in a small package, exploiting the condensed genome of Ciona intestinalis
Abstract
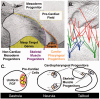
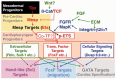
Defects in the initial establishment of cardiogenic cell fate are likely to contribute to pervasive human congenital cardiac abnormalities. However, the molecular underpinnings of nascent cardiac fate induction have proven difficult to decipher. In this review we explore the participation of extracellular, cellular and nuclear factors in comprehensive specification networks. At each level, we elaborate on insights gained through the study of cardiogenesis in the invertebrate chordate Ciona intestinalis and propose productive lines of future research. In-depth discussion of pre-cardiac induction is intended to serve as a paradigm, illustrating the potential use of Ciona to elucidate comprehensive networks underlying additional aspects of chordate cardiogenesis, including directed migration and subspecification of cardiac and pharyngeal lineages.
Keywords: FGF; Mesp; cardiac induction; chordate evolution; extracellular matrix; gene regulatory networks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ciona intestinalis as a model for cardiac development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007 Feb;18(1):16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2006.12.007. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17223594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initial deployment of the cardiogenic gene regulatory network in the basal chordate, Ciona intestinalis.Dev Biol. 2012 Aug 1;368(1):127-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.05.002. Epub 2012 May 14. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22595514 Free PMC article.
-
FGF signaling delineates the cardiac progenitor field in the simple chordate, Ciona intestinalis.Genes Dev. 2006 Oct 1;20(19):2728-38. doi: 10.1101/gad.1467706. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17015434 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulatory networks for the development and evolution of the chordate heart.Genes Dev. 2006 Oct 1;20(19):2634-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1485706. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17015427 Review. No abstract available.
-
Unraveling genomic regulatory networks in the simple chordate, Ciona intestinalis.Genome Res. 2005 Dec;15(12):1668-74. doi: 10.1101/gr.3768905. Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 16339364 Review.
Cited by
-
Fibronectin contributes to notochord intercalation in the invertebrate chordate, Ciona intestinalis.Evodevo. 2016 Aug 31;7(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13227-016-0056-4. eCollection 2016. Evodevo. 2016. PMID: 27583126 Free PMC article.
-
Lhx3/4 initiates a cardiopharyngeal-specific transcriptional program in response to widespread FGF signaling.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jan 25;22(1):e3002169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002169. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38271304 Free PMC article.
-
Architectural delineation and molecular identification of extracellular matrix in ascidian embryos and larvae.Biol Open. 2017 Sep 15;6(9):1383-1390. doi: 10.1242/bio.026336. Biol Open. 2017. PMID: 28916708 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and evolution of muscle development in tunicates.Evodevo. 2019 Jun 24;10:13. doi: 10.1186/s13227-019-0125-6. eCollection 2019. Evodevo. 2019. PMID: 31249657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation and evolution of cardiopharyngeal cell identity and behavior: insights from simple chordates.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015 Jun;32:119-28. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015. PMID: 25819888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Waddington CH. Organisers and Genes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1940.
-
- Waddington CH. The Strategy of the Genes. London: Allen & Unwin; 1957.
-
- Satō N. Developmental biology of ascidians. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1994.
-
- Delsuc F, Brinkmann H, Chourrout D, et al. Tunicates and not cephalochordates are the closest living relatives of vertebrates. Nature. 2006;439:965–8. - PubMed
-
- Satou Y. The ascidian Mesp gene specifies heart precursor cells. Development. 2004;131:2533–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

