Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays for Myc and N-Myc
- PMID: 24006062
- PMCID: PMC4349432
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-429-6_9
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays for Myc and N-Myc
Abstract
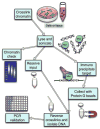
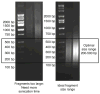
Myc and N-Myc have widespread impacts on the chromatin state within cells, both in a gene-specific and genome-wide manner. Our laboratory uses functional genomic methods including chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), ChIP-chip, and, more recently, ChIP-seq to analyze the binding and genomic location of Myc. In this chapter, we describe an effective ChIP protocol using specific validated antibodies to Myc and N-Myc. We discuss the application of this protocol to several types of stem and cancer cells, with a focus on aspects of sample preparation prior to library preparation that are critical for successful Myc ChIP assays. Key variables are discussed and include the starting quantity of cells or tissue, lysis and sonication conditions, the quantity and quality of antibody used, and the identification of reliable target genes for ChIP validation.
Figures

References
-
- Guccione E, Martinato F, Finocchiaro G, Luzi L, Tizzoni L, Dall’ Olio V, et al. Myc-binding-site recognition in the human genome is determined by chromatin context. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:764–770. - PubMed
-
- Staller P, Peukert K, Kiermaier A, Seoane J, Lukas J, Karsunky H, et al. Repression of p15INK4b expression by Myc through association with Miz-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:392–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

