Aluminum hydroxide influences not only the extent but also the fine specificity and functional activity of antibody responses to tick-borne encephalitis virus in mice
- PMID: 24006434
- PMCID: PMC3807910
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01690-13
Aluminum hydroxide influences not only the extent but also the fine specificity and functional activity of antibody responses to tick-borne encephalitis virus in mice
Abstract
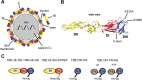
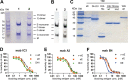
Aluminum hydroxide is the most widely used adjuvant in human vaccines and serves as a potent enhancer of antibody production. Its stimulatory effect strongly depends on the adsorption of the antigen to the adjuvant, which may influence antigen presentation and, as a consequence, the fine specificity of antibody responses. Such variations can have functional consequences and can modulate the effectiveness of humoral immunity. Therefore, we investigated the influence of aluminum hydroxide on the fine specificity of antibody responses in a model study in mice using an inactivated purified virus particle, the flavivirus tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus, as an immunogen. To dissect and quantify the specificities of polyclonal antibodies in postimmunization sera, we established a platform of immunoassays using recombinant forms of the major target of neutralizing antibodies (protein E) as well as individual domains of E (DIII and the combination of DI and DII [DI+DII]). Our analyses revealed a higher proportion of neutralizing than virion binding (as detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) antibodies after immunization with aluminum hydroxide. Furthermore, the induction of antibodies to DIII, a known target of potently neutralizing antibodies, as well as their contributions to virus neutralization were significantly greater in mice immunized with adjuvant and correlated with a higher avidity of these antibodies. Thus, our data provide evidence that aluminum hydroxide can lead to functionally relevant modulations of antibody fine specificities in addition to its known overall immune enhancement effect.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunization with Immune Complexes Modulates the Fine Specificity of Antibody Responses to a Flavivirus Antigen.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7970-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00938-15. Epub 2015 May 27. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26018152 Free PMC article.
-
Variation of the specificity of the human antibody responses after tick-borne encephalitis virus infection and vaccination.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(23):13845-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02086-14. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25253341 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant domains III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus envelope protein in combination with dextran and CpGs induce immune response and partial protectiveness against TBE virus infection in mice.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 7;16(1):544. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1884-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27717318 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Evaluation of Antivirals and Neutralizing Antibodies Against Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2936:125-136. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4587-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40512316
-
After a tick bite in a tick-borne encephalitis virus endemic area: current positions about post-exposure treatment.Vaccine. 2008 Feb 13;26(7):863-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.11.046. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18206274 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunization with Immune Complexes Modulates the Fine Specificity of Antibody Responses to a Flavivirus Antigen.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7970-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00938-15. Epub 2015 May 27. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26018152 Free PMC article.
-
Specificities of human CD4+ T cell responses to an inactivated flavivirus vaccine and infection: correlation with structure and epitope prediction.J Virol. 2014 Jul;88(14):7828-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00196-14. Epub 2014 Apr 30. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24789782 Free PMC article.
-
Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells at the crossroad of type I interferon-regulated B cell differentiation and antiviral response to tick-borne encephalitis virus.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Apr 15;17(4):e1009505. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009505. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33857267 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Characterization of the Innate Immune Pathways Engaged by Live and Inactivated Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;9(6):664. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060664. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204532 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive flavivirus E trimer breathing accompanies stem zippering of the post-fusion hairpin.EMBO Rep. 2020 Aug 5;21(8):e50069. doi: 10.15252/embr.202050069. Epub 2020 Jun 2. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 32484292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA. 2013. Vaccines, 6th ed. Saunders Elsevier, San Diego, CA
-
- Grun JL, Maurer PH. 1989. Different T helper cell subsets elicited in mice utilizing two different adjuvant vehicles: the role of endogenous interleukin 1 in proliferative responses. Cell Immunol. 121:134–145 - PubMed
-
- Morefield GL, Sokolovska A, Jiang D, HogenEsch H, Robinson JP, Hem SL. 2005. Role of aluminum-containing adjuvants in antigen internalization by dendritic cells in vitro. Vaccine 23:1588–1595 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

