Targeted inactivation of β1 integrin induces β3 integrin switching, which drives breast cancer metastasis by TGF-β
- PMID: 24006485
- PMCID: PMC3814150
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-10-0776
Targeted inactivation of β1 integrin induces β3 integrin switching, which drives breast cancer metastasis by TGF-β
Erratum in
- Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Feb;25(4):548
Abstract
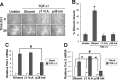
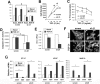
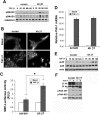
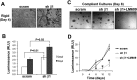
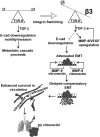
Mammary tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) programs cooperate in converting transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) from a suppressor to a promoter of breast cancer metastasis. Although previous reports associated β1 and β3 integrins with TGF-β stimulation of EMT and metastasis, the functional interplay and plasticity exhibited by these adhesion molecules in shaping the oncogenic activities of TGF-β remain unknown. We demonstrate that inactivation of β1 integrin impairs TGF-β from stimulating the motility of normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells (MECs) and elicits robust compensatory expression of β3 integrin solely in malignant MECs, but not in their normal counterparts. Compensatory β3 integrin expression also 1) enhances the growth of malignant MECs in rigid and compliant three-dimensional organotypic cultures and 2) restores the induction of the EMT phenotypes by TGF-β. Of importance, compensatory expression of β3 integrin rescues the growth and pulmonary metastasis of β1 integrin-deficient 4T1 tumors in mice, a process that is prevented by genetic depletion or functional inactivation of β3 integrin. Collectively our findings demonstrate that inactivation of β1 integrin elicits metastatic progression via a β3 integrin-specific mechanism, indicating that dual β1 and β3 integrin targeting is necessary to alleviate metastatic disease in breast cancer patients.
Figures



References
-
- Bei L, Lu Y, Bellis SL, Zhou W, Horvath E, Eklund EA. Identification of a HoxA10 activation domain necessary for transcription of the gene encoding b3 integrin during myeloid differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:16846–16859. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ze'ev A. The dual role of cytoskeletal anchor proteins in cell adhesion and signal transduction. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;886:37–47. - PubMed
-
- Bhowmick NA, Zent R, Ghiassi M, McDonnell M, Moses HL. Integrin b1 signaling is necessary for transforming growth factor-b activation of p38MAPK and epithelial plasticity. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:46707–46713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

