Lung-resident memory CD8 T cells (TRM) are indispensable for optimal cross-protection against pulmonary virus infection
- PMID: 24006506
- PMCID: PMC3896663
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0313180
Lung-resident memory CD8 T cells (TRM) are indispensable for optimal cross-protection against pulmonary virus infection
Abstract
Previous studies have shown that some respiratory virus infections leave local populations of tissue TRM cells in the lungs which disappear as heterosubtypic immunity declines. The location of these TRM cells and their contribution to the protective CTL response have not been clearly defined. Here, fluorescence microscopy is used to show that some CD103(+) TRM cells remain embedded in the walls of the large airways long after pulmonary immunization but are absent from systemically primed mice. Viral clearance from the lungs of the locally immunized mice precedes the development of a robust Teff response in the lungs. Whereas large numbers of virus-specific CTLs collect around the bronchial tree during viral clearance, there is little involvement of the remaining lung tissue. Much larger numbers of TEM cells enter the lungs of the systemically immunized animals but do not prevent extensive viral replication or damage to the alveoli. Together, these experiments show that virus-specific antibodies and TRM cells are both required for optimal heterosubtypic immunity, whereas circulating memory CD8 T cells do not substantially alter the course of disease.
Keywords: cellular immunity; fluorescence microscopy; immunization; influenza virus.
Figures

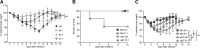

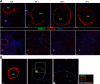
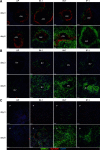

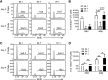
Comment in
-
Editorial: Pulmonary resident memory CD8 T cells: here today, gone tomorrow.J Leukoc Biol. 2014 Feb;95(2):199-201. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0913493. J Leukoc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24482485 No abstract available.
References
-
- Topham D. J., Tripp R. A., Doherty P. C. (1997) CD8+ T cells clear influenza virus by perforin or Fas-dependent processes. J. Immunol. 159, 5197–5200 - PubMed
-
- Liang S., Mozdzanowska K., Palladino G., Gerhard W. (1994) Heterosubtypic immunity to influenza type A virus in mice. Effector mechanisms and their longevity. J. Immunol. 152, 1653–1661 - PubMed
-
- Nguyen H. H., Moldoveanu Z., Novak M. J., van Ginkel F. W., Ban E., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. (1999) Heterosubtypic immunity to lethal influenza A virus infection is associated with virus-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses induced in mucosa-associated tissues. Virology 254, 50–60 - PubMed
-
- Kreijtz J. H., Bodewes R., van Amerongen G., Kuiken T., Fouchier R. A., Osterhaus A. D., Rimmelzwaan G. F. (2007) Primary influenza A virus infection induces cross-protective immunity against a lethal infection with a heterosubtypic virus strain in mice. Vaccine 25, 612–620 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

